- Products
Network & SASE IoT Protect Maestro Management OpenTelemetry/Skyline Remote Access VPN SASE SD-WAN Security Gateways SmartMove Smart-1 Cloud SMB Gateways (Spark) Threat PreventionCloud Cloud Network Security CloudMates General CloudGuard - WAF Talking Cloud Podcast Weekly ReportsSecurity Operations Events External Risk Management Incident Response Infinity AI Infinity Portal NDR Playblocks SOC XDR/XPR Threat Exposure Management
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- AI Security
- Developers & More
- Check Point Trivia
- CheckMates Toolbox
- General Topics
- Products Announcements
- Threat Prevention Blog
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
Check Point
for Beginners
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Educational Resources
- :
- Check Point for Beginners
- :
- Part 4 - Installing Security Gateway
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
OPEN OTHER ARTICLES
 Part 1 - The Architecture
Part 1 - The Architecture
 Part 2 - Preparing the Lab
Part 2 - Preparing the Lab
 Part 3 - Installing Security Management Server
Part 3 - Installing Security Management Server
 Part 5 - Gaia WebUI and CLI
Part 5 - Gaia WebUI and CLI
 Part 6 - Working with SmartConsole
Part 6 - Working with SmartConsole
 Part 7 - Managing Security Policies
Part 7 - Managing Security Policies
 Part 8 - Network Address Translation
Part 8 - Network Address Translation
 Part 9 - Application Control, URL Filtering and Content Awareness
Part 9 - Application Control, URL Filtering and Content Awareness
 Part 10 - Identity Awareness
Part 10 - Identity Awareness
 Part 11 - Threat Prevention
Part 11 - Threat Prevention
 Part 12 - Logs and Reporting
Part 12 - Logs and Reporting
 Site to Site VPN in R80.x - Tutorial for Beginners
Site to Site VPN in R80.x - Tutorial for Beginners
 Absolute Beginner’s Guide to R80.x
Absolute Beginner’s Guide to R80.x
 Handling Traffic in the Access Policy - Knowledge Nuggets
Handling Traffic in the Access Policy - Knowledge Nuggets
 Video - Security Administration Experience
Video - Security Administration Experience
 Video - Securing Hybrid Cloud Environment
Video - Securing Hybrid Cloud Environment
 Video - Smart-1 Cloud - Cloud Based Security Management
Video - Smart-1 Cloud - Cloud Based Security Management
 Video - Container Security
Video - Container Security
 Video - Identity Based Segmentation
Video - Identity Based Segmentation
 Video - Securing Public Cloud Environment
Video - Securing Public Cloud Environment
 Video - Threat Hunting, Detection, and Monitoring
Video - Threat Hunting, Detection, and Monitoring
 Video - Firewall as a Service (FWaaS)
Video - Firewall as a Service (FWaaS)
 Video - Application Control and URL Filtering
Video - Application Control and URL Filtering
 Video - TLS Inspection
Video - TLS Inspection
 Video - Hyper Scale Clustering with Quantum Maestro
Video - Hyper Scale Clustering with Quantum Maestro
 Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Introduction
Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Introduction
 Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI
Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI
 Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - SmartConsole
Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - SmartConsole
 Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI Part 2
Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI Part 2
 Network Security
Network Security
PREVIOUS ARTICLE
TO READ THE FULL POST
it's simple and free
NEXT ARTICLE
Part 4 - Installing Security Gateway
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
2020-06-11
04:32 AM
In this lecture, we will cover deployment and initial configuration of a Security Gateway.
Deployment
As mentioned in our first lecture, Security Gateway can be deployed in three different options:
- Check Point Security Appliance;
- Open Server;
- A Virtual Machine.
Note: in the practical part of this lecture, we will be installing our lab Security Gateway as a virtual machine.
Check Point Security Appliance
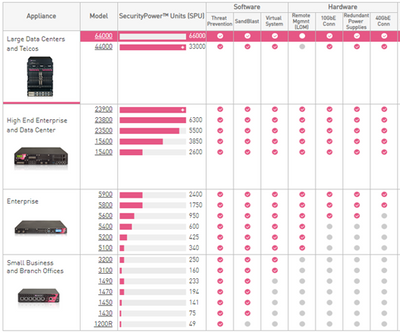
With Check Point, there are four categories of Security Gateway Appliances:
- Small and Medium Business,
- Enterprise,
- High End Enterprise and Data Center,
- Large Data Centers and Telcos, also known as Scalable Platforms (SP).
Note: SMB and SP appliances use different OS and software and are not part of our discussion.
Similar to what we have noted previously for the case of Smart-1 deployment, Check Point Security Gateway comes preinstalled with at least one version of Check Point Gaia software. If you want to re-image the appliance or install a software version different from the available factory defaults, look into sk65205.
Open Server / virtual machine
If you are deploying your Security Gateway on an Open Server or as a virtual machine, consult with the Hardware Compatibility List to make sure your deployment option is supported by Check Point. Installation flow for open server and a virtual machine is practically identical.
Installing a Software Gateway
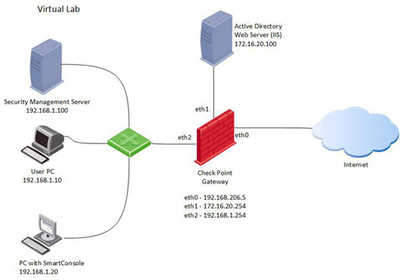
In our lab, we will be installing a Security Gateway as a virtual machine. Let us review the lab configuration:
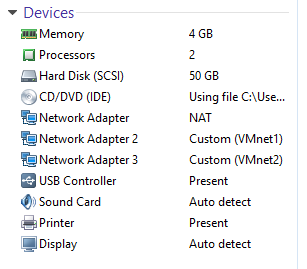
Create a new virtual machine with the following parameters:
Note there are three different NICs defined. The initial installation flow is very similar to the Management Server installation covered in the previous lecture. The only difference is about configuring interfaces.
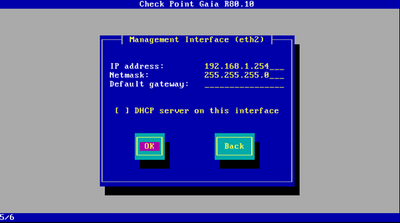
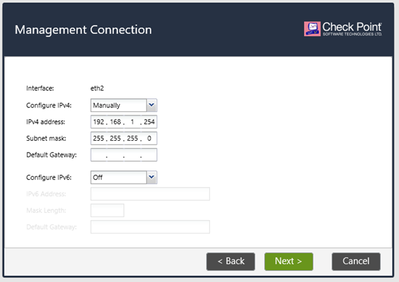
At this step, choose NIC that shares a network with Lab User PC (VMnet2). In our case, it is eth2. Set up IP as 192.168.1.254/24 and leave Default gateway settings empty.
Continue the installation and reboot.
Initializing Security Gateway
Initialization process is very similar for any Gaia based deployment: an appliance or open server, management or gateway. You are already familiar with the process from the last lecture.
In your browser, connect to https://192.168.1.254 and login with admin user and the password you have defined during installation process (vpn123 in our case). Start the First Time Configuration Wizard and choose “Continue with R80.10 configuration”.
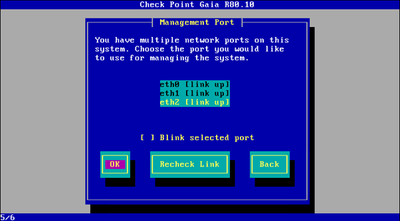
Leave interface eth2 settings as is.
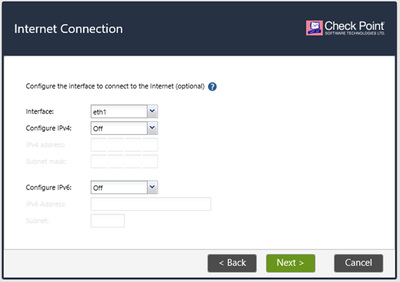
Wizard will advise you to set up other interfaces. Skip them at this point by pressing Next. We will set up other networks later on.
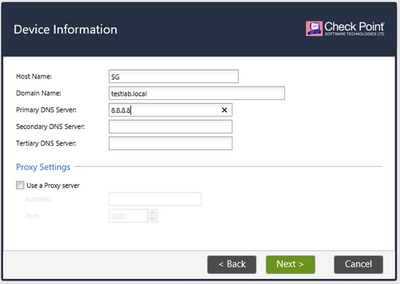
In Device Information menu, set up the machine hostname (SG), domain name (testlab.local) and the Primary DNS Server (8.8.8.8):
Leave Date and Time as default and press Next.
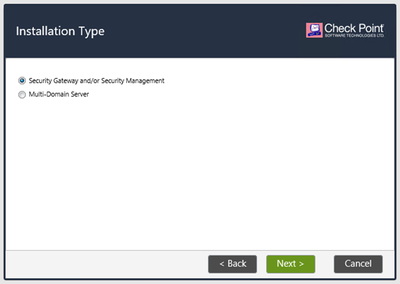
Choose “Security Gateways and/or Security Management” for Installation Type and press и Next:
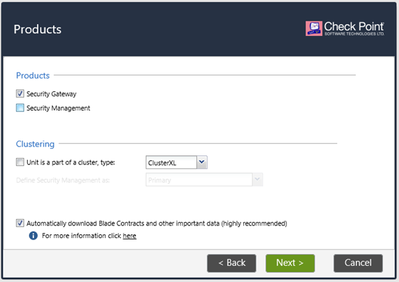
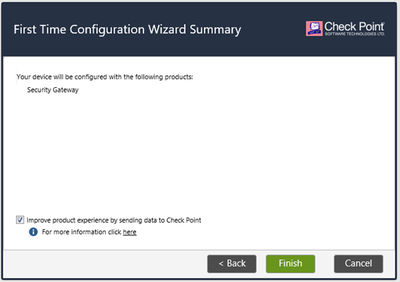
For Products, chose only Security Gateway. Press Next to continue.
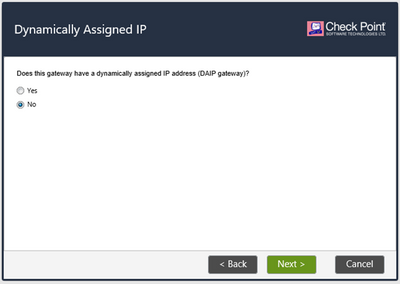
Choose No for Dynamically Assigned IP (DIAP) and press Next:
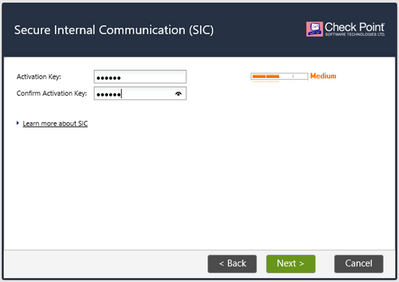
The last part of the Wizard is about SIC – Secure Internal Communication. In a few words, all parts of Check Point based Security System are using TLS encrypted channel to interconnect. This tunnel is known as SIC. It uses certificate based encryption. Certificates are issued by the Management Server and are initialized with an activation key we are defining at this step.
For further information about SIC, feel free to click on “learn more about SIC” link in the menu.
Press Finish to conclude the initialization process. The machine will reboot.
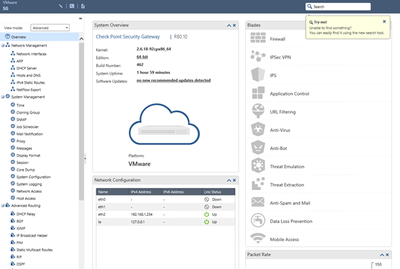
After reboot, you will be able to login into Gaia WebUI, same as in the case of SMS in the previous lecture.
Congratulations, you have successfully finished installation and initial configuration of two major elements of Check Point security system: Security Management and Security Gateway.
Next time we will continue configuring our system and will work with Gaia WebUI and CLI.
Labels
In this lecture, we will cover deployment and initial configuration of a Security Gateway.
Deployment
As mentioned in our first lecture, Security Gateway can be deployed in three different options:
- Check Point Security Appliance;
- Open Server;
- A Virtual Machine.
Note: in the practical part of this lecture, we will be installing our lab Security Gateway as a virtual machine.
Check Point Security Appliance
With Check Point, there are four categories of Security Gateway Appliances:
- Small and Medium Business,
- Enterprise,
- High End Enterprise and Data Center,
- Large Data Centers and Telcos, also known as Scalable Platforms (SP).
Note: SMB and SP appliances use different OS and software and are not part of our discussion.
Similar to what we have noted previously for the case of Smart-1 deployment, Check Point Security Gateway comes preinstalled with at least one version of Check Poi
...
2 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
About CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter