- Products
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- AI Security
- Developers & More
- Check Point Trivia
- CheckMates Toolbox
- General Topics
- Products Announcements
- Threat Prevention Blog
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
Check Point
for Beginners
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Educational Resources
- :
- Check Point for Beginners
- :
- Part 1 - The Architecture
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
OPEN OTHER ARTICLES
 Part 2 - Preparing the Lab
Part 2 - Preparing the Lab
 Part 3 - Installing Security Management Server
Part 3 - Installing Security Management Server
 Part 4 - Installing Security Gateway
Part 4 - Installing Security Gateway
 Part 5 - Gaia WebUI and CLI
Part 5 - Gaia WebUI and CLI
 Part 6 - Working with SmartConsole
Part 6 - Working with SmartConsole
 Part 7 - Managing Security Policies
Part 7 - Managing Security Policies
 Part 8 - Network Address Translation
Part 8 - Network Address Translation
 Part 9 - Application Control, URL Filtering and Content Awareness
Part 9 - Application Control, URL Filtering and Content Awareness
 Part 10 - Identity Awareness
Part 10 - Identity Awareness
 Part 11 - Threat Prevention
Part 11 - Threat Prevention
 Part 12 - Logs and Reporting
Part 12 - Logs and Reporting
 Site to Site VPN in R80.x - Tutorial for Beginners
Site to Site VPN in R80.x - Tutorial for Beginners
 Absolute Beginner’s Guide to R80.x
Absolute Beginner’s Guide to R80.x
 Handling Traffic in the Access Policy - Knowledge Nuggets
Handling Traffic in the Access Policy - Knowledge Nuggets
 Video - Security Administration Experience
Video - Security Administration Experience
 Video - Securing Hybrid Cloud Environment
Video - Securing Hybrid Cloud Environment
 Video - Smart-1 Cloud - Cloud Based Security Management
Video - Smart-1 Cloud - Cloud Based Security Management
 Video - Container Security
Video - Container Security
 Video - Identity Based Segmentation
Video - Identity Based Segmentation
 Video - Securing Public Cloud Environment
Video - Securing Public Cloud Environment
 Video - Threat Hunting, Detection, and Monitoring
Video - Threat Hunting, Detection, and Monitoring
 Video - Firewall as a Service (FWaaS)
Video - Firewall as a Service (FWaaS)
 Video - Application Control and URL Filtering
Video - Application Control and URL Filtering
 Video - TLS Inspection
Video - TLS Inspection
 Video - Hyper Scale Clustering with Quantum Maestro
Video - Hyper Scale Clustering with Quantum Maestro
 Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Introduction
Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Introduction
 Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI
Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI
 Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - SmartConsole
Video - Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - SmartConsole
 Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI Part 2
Check Point R81.X - Crash Course - Admin GUI Part 2
 Network Security
Network Security
Part 1 - The Architecture
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
2020-06-11
04:10 AM
Introduction
Check Point Software Technologies (Check Point for short) is a company operating exclusively on the field of Information Security and covering four main areas:
- Network Security on the perimeter and inside Data Centers.
- Cloud Security: Public, Private and Hybrid.
- Endpoint Security for both Windows and Macs.
- Mobile Security for Android and iOS devices.
In this article, we are discussing Network Security solutions with Check Point.
Network Defense. Three Tier Architecture components
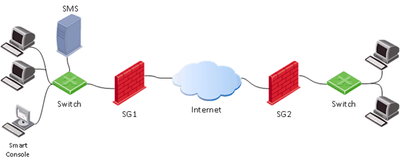
The main product of Check Point is the network security solution – Next Generation Firewall (NGFW). When working with it, you will encounter three main components: Security Gateway, Security Management Server and SmartConsole.
- Security Gateway (SG) is usually deployed on the perimeter to control and secure traffic with Firewall and Threat Prevention capabilities.
- Security Management Server (SMS) defines and controls security policies on the Gateways. It can also be used to as a log server with built-in system of log indexing (SmartLog) and event correlation (SmartEvent – a SIEM-like solution for Check Point products). Usually, SMS is the main element of central management with multiple Security Gateways in operation. Nevertheless, you need an SMS even if your security system has a single gateway only.
- SmartConsole is a GUI administration tool to connect to SMS. Through this tool, a security administrator is able to prepare and apply security policies to the Security Gateways.
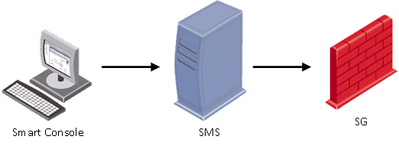
Administration process includes the following steps:
- Security Administrator opens SmartConsole and connects to the Security Management Server.
- Security Administrator changes the existing (or defines a new) security policy and applies the changing by pressing Install Policy button.
- Security Management Server verifies policy for consistency to avoid logical errors, compiles it and send the result policy package to a Security Gateway.
- Security Gateway receives the compiled policy and applies it to the network traffic crossing the gateway.
Operating Systems
Historically, Check Point Software Technologies was oriented to different OSs: SUN, AIX, HP-OS, various flavors of Linux and Windows, IPSO, Secure Platform (SPLAT) and others. Today three component of Check Point are using the following Operating Systems:
- Windows – for SmartConsole only. SG and SMS cannot be deployed on Windows.
- Gaia – Check Point own OS based on hardened RH Enterprise Linux. Gaia will be the focus of some further materials, as it is the main option when deploying both SMS and SG on open server platform and Check Point appliances.
Note: Check Point SMB appliances based on ARM processors are using Gaia Embedded OS, which is a stripped and optimized version of Gaia.
Software Versions
At this moment Check Point supports three main software versions of its products:
- R77.30
- R80.10
- R80.20
R77.30 is planned to go out of support in May 2019. R80.20 was released at the end of September 2018.
Deployment option
There are different deployment options for a Network Security System based on Check Point products:
- Check Point Security Appliance. This option includes both hardware and software required to run Check Point Network Security System.
- Open Server. Gaia OS can be deployed on specific certified servers from a Hardware Compatibility List available on Check Point web site.
- A Virtual Machine. Gaia supports VMware ESX and the most popular public cloud platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba, and Oracle.
Standalone and Distributed Deployment
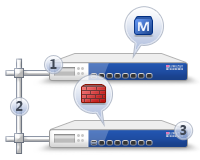
Security Gateway and Security Management Server components can be deployed on the same hardware of VM (Standalone):
or as different entities (Distributed Deployment).
Standalone option is economical but also limited, especially when talking about performance.
Distributed is the most popular and deployment option for Check Point customers. For some specific functions, such as SmartEvent, distributed deployment is a requirement.
Gateway Deployment
Security Gateway is deployed in a Routed Mode or a Bridge Mode.
Routed Mode is the most common. In this case, Security Gateway performs L3 routing when forwarding traffic allowed by Security Policy.
Bridge Mode can be deployed without changing network topology, to control traffic on Layer 2. Some functionality is limited in this mode.
Check Point Software Blades
One of the most frequent questions beginners have is about the term “Software Blades”. In plain words, Check Point is using this term for specific features of its products.
Security Gateways and Management Servers have collections of related Software Blades that one can enable or disable when required, depending on licensing. Combination of those defines specific flavor of Check Point products.
We will be addressing most of the Software Blades and their functions in the further CP4B materials. However, it worth listing all Software Blades available for Management and Gateways here.
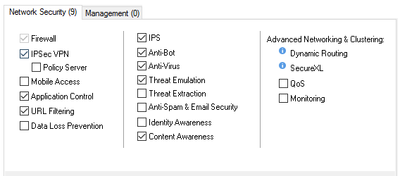
Security Gateway Software Blades
- Firewall – Basic security filtering functionality
- IPSec VPN – functionality for creating IPSec-based Site to Site Virtual Private Networks
- Mobile Access – SSL and IPSec Endpoint VPN solution
- Application Control & URL Filtering – Advanced Security solution to control Web URL and Application traffic through the gateway
- Data Loss Prevention – Pre-emptively prevent sensitive information from leaving the organization, educate users on proper data handling procedures, and allow remediation in real-time
- IPS – Intrusion Prevention System
- Anti-Bot – blade to detect and prevent Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) activity within the protected network
- Anti-Virus – AVI scanning on the fly for downloads and uploads crossing Security Gateways
- Threat Emulation – Sandboxing solution for downloads and email attachments
- Threat Extraction – Unique technique to remove active content from downloads and attachments to prevent incidental malware infections and APT
- AntiSpam & Email Security – email protection blade
- Identity Awareness – Provides visibility to the identities of end users and the specific Active Directory host they are connecting from. This allows security policies to be enforced based on any combination of user, specific machine, or network.
- Content Awareness – Control over specific types of content data files crossing Security Gateways
- QoS – Quality of Service, traffic shaping and prioritization functionality
- Monitoring – Real Time Monitoring of performance and traffic indicators for Security Gateways
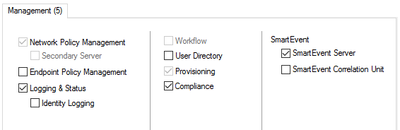
Security Management Server Software Blades
- Network Policy Management — to create and manage SG security policies
- Endpoint Policy Management — to create and manage Endpoint Security Policies
- Logging & Status – central logging and log consolidation functionality
- Workflow — Change Management Cycle functionality with ability to audit and approve certain policy management operations
- User Directory — User management and integration with external authentication solutions
- Provisioning — Centralized maintenance tool
- Compliance — Automated compliance tool for security and best practices audits
- SmartEvent — Log correlation and Security Events management tool
Conclusion
In this article we have introduce you to the main terms and concepts of Check Point Network Security product family. In the next articles, we will address installation and initial configuration flow for both Security Gateway and Security Management Server.
----------------------------
Authors and Contributors
Author - Evgeniy Olkov, CTO at TS Solution.
Founded in 2010, the TS Solution is a fast growing Russian company, focused on integrating high-tech networking, security and server virtualization systems and technologies, along with maintenance and professional services.
Translation and editing - Valeri Loukine
Review and editing - Dameon Welch-Abernathy
Labels
Introduction
Check Point Software Technologies (Check Point for short) is a company operating exclusively on the field of Information Security and covering four main areas:
- Network Security on the perimeter and inside Data Centers.
- Cloud Security: Public, Private and Hybrid.
- Endpoint Security for both Windows and Macs.
- Mobile Security for Android and iOS devices.
In this article, we are discussing Network Security solutions with Check Point.
Network Defense. Three Tier Architecture components
The main product of Check Point is the network security solution – Next Generation Firewall (NGFW). When working with it, you will encounter three main components: Security Gateway, Security Management Server and SmartConsole.
- Security Gateway (SG) is usually deployed on the perimeter to control and secure traffic with Firewall and Threat Prevention capabilities.
- Security Management Server (SMS) de
22 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
About CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter