- Products
Network & SASE IoT Protect Maestro Management OpenTelemetry/Skyline Remote Access VPN SASE SD-WAN Security Gateways SmartMove Smart-1 Cloud SMB Gateways (Spark) Threat PreventionCloud Cloud Network Security CloudMates General CloudGuard - WAF Talking Cloud Podcast Weekly ReportsSecurity Operations Events External Risk Management Incident Response Infinity AI Infinity Portal NDR Playblocks SOC XDR/XPR Threat Exposure Management
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- AI Security
- Developers & More
- Check Point Trivia
- CheckMates Toolbox
- General Topics
- Products Announcements
- Threat Prevention Blog
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
CheckMates Fest 2026
Join the Celebration!
AI Security Masters
E1: How AI is Reshaping Our World
MVP 2026: Submissions
Are Now Open!
What's New in R82.10?
Watch NowOverlap in Security Validation
Help us to understand your needs better
CheckMates Go:
Maestro Madness
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Products
- :
- Network & SASE
- :
- Security Gateways
- :
- Disable/enable Anti-spoofing globally on security ...
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Are you a member of CheckMates?
×
Sign in with your Check Point UserCenter/PartnerMap account to access more great content and get a chance to win some Apple AirPods! If you don't have an account, create one now for free!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Disable/enable Anti-spoofing globally on security gateway
Hello,
Is there a way to disable/enable Anti-spoofing globally on a security gateway rather than doing it specifically on each and every interface? R80.10
6 Replies
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yes, there is. Just install our ccc script and select the specific option within the Firewall Gateway menu.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks Danny,
Should this script install on each gateway or only on the management server?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Install it on each gateway. Additionally you can also install it on your management for the management functions it offers. Keep in mind that changing the Anti-spoofing this way might not survive reboots out-of-the-box.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thakns,
I have installed it on one of our gateways Clusters , run this command on both Cluster members from the script and installed policy but still, I can see Anti-spoofing logs
fw ctl set int fw_antispoofing_enabled 0 ; fwaccel off; fwaccel on
Am I missing something?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
For R80.10 and earlier the commands to disable anti-spoofing "on the fly" are:
fw ctl set int fw_antispoofing_enabled 0
sim feature anti_spoofing off; fwaccel off; fwaccel on
Because you were missing the sim feature command SecureXL was still enforcing antispoofing.
For R80.20 Jumbo HFA Take 103+ and R80.30 Jumbo HFA Take 71+, the following is taken from the third edition of my book; this topic is not directly related to performance but I felt it was important enough to cover due to the dire consequences of making a mistake:
Click to Expand
Watch Out: Antispoofing Enforcement
Antispoofing ensures that traffic is flowing the “correct” way through the firewall,
based on the packet’s source IP address upon ingress to the firewall, and the packet’s
destination IP address upon egress of the firewall. Antispoofing is a separate
enforcement mechanism that is consulted long before any policy layers. Based on the
recommendations in this chapter, you may need to make firewall topology adjustments to
ensure traffic is being inspected efficiently by the firewall. Antispoofing relies heavily
on the firewall’s topology definitions for proper enforcement. If you are not familiar
with the antispoofing feature or its ramifications, I’d strongly recommend checking out
the CheckMates post located here: A Primer on Anti-Spoofing.
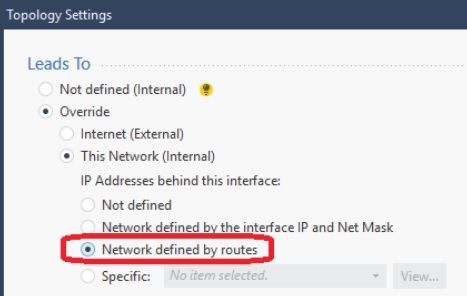
Note that in R80.20 or later firewalls a new dynamic option for calculating
antispoofing topology for an interface has been introduced, called “Network defined by
routes”:
Figure 8-89: New “Network defined by routes” Setting on R80.20+ Firewalls
When selected this option will automatically define the topology for the interface
based on all directly-connected, static, and dynamic routes referencing that interface. So
therefore if any antispoofing issues are encountered, the actual problem is probably a
missing route which can be much easier to troubleshoot.
If you have inherited an existing firewall deployment, or are otherwise unfamiliar
with its network topology configuration, making sense of the firewall’s defined topology
from the SmartConsole GUI can be difficult. Nested network groups, a separate screen
for every interface, and a multitude of anti-spoofing related settings for each individual
interface can make forming a mental picture of your network and its topology a truly
daunting task. To make things even more difficult, the firewall’s topology cannot be
easily viewed from the Management CLI/API interface either.
However CheckMates user Danny Jung has created a special CLI tool called “One-
liner for Address Spoofing Troubleshooting” (which won an award for 2019 CheckMates
Code Hub Contribution of the Year) that provides a no-nonsense, text-based dump of the
firewall’s topology and associated antispoofing settings from the CLI. Not only is this
tool useful for troubleshooting antispoofing problems, but is great for figuring out the
actual working topology of your firewall. The tool is located at CheckMates here: One-
liner for Address Spoofing Troubleshooting.
WARNING: If you determine that there are missing interfaces in your
firewall’s topology definition, you might be tempted to click the “Get Interfaces” button
on the Network Management screen of the firewall object in the SmartConsole. But
before you do that, look carefully at the Get Interfaces button after clicking it. Note that
it provides two possible choices when left-clicked (“Get Interfaces With Topology” and
“Get Interfaces Without Topology”). Clicking the “Get Interfaces Without Topology”
menu choice is the appropriate one to use in this case to add any missing interfaces.
Clicking “Get Interfaces With Topology” will attempt to modify the interface topology
definition of all existing interfaces as well, which may impact anti-spoofing enforcement,
which could cause a huge outage and even disrupt your ability to manage the firewall!
Even if you choose the proper “Get Interfaces Without Topology” option, you should
ALWAYS manually verify the topology of ALL interfaces afterward prior to installing the
policy!
Should you find yourself cut off from managing or installing policy to the firewall
due to misconfigured anti-spoofing enforcement, run these expert mode commands on a
R80.30 Jumbo HFA Take 71+ firewall to disable antispoofing “on the fly”, and recover
the ability to install a corrected policy (the second line assumes that SecureXL is
currently enabled on the firewall):
fw ctl set int fw_antispoofing_enabled 0
fw ctl set int sim_anti_spoofing_enabled 0 -a
Gaia 4.18 (R82) Immersion Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Video Course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks, that worked.
Leaderboard
Epsum factorial non deposit quid pro quo hic escorol.
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 21 | |
| 19 | |
| 11 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |
Upcoming Events
Thu 08 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 1: How AI is Reshaping Our WorldThu 22 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 2: Hacking with AI: The Dark Side of InnovationThu 12 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 3: Exposing AI Vulnerabilities: CP<R> Latest Security FindingsThu 26 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 4: Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloudThu 08 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 1: How AI is Reshaping Our WorldThu 22 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 2: Hacking with AI: The Dark Side of InnovationThu 26 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 4: Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloudAbout CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter