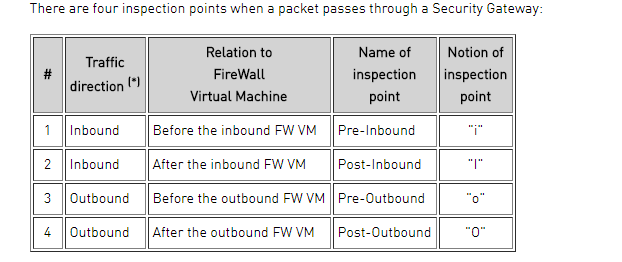
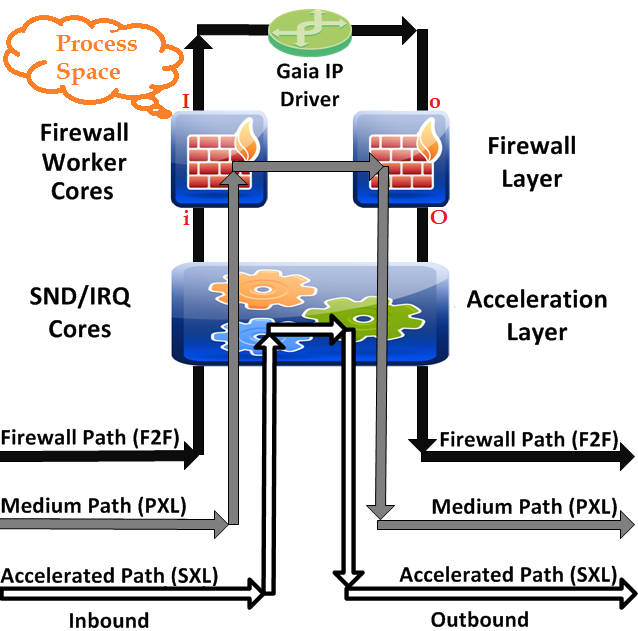
in chain refers to what happens between "little i" and "big I".
out chain refers to what happens between "little o" and "big O".
fw is the access policy.
Anti-spoofing I believe is done as part of stateless verifications.
[Expert@R8010:0]# fw ctl chain
in chain (17):
0: -7ffffff0 (ffffffff8903d8d0) (00000001) tcpt inbound (tcp_tun)
1: -7f800000 (ffffffff88877f40) (ffffffff) IP Options Strip (in) (ipopt_strip)
2: - 2000000 (ffffffff89018bb0) (00000003) vpn decrypt (vpn)
3: - 1fffffa (ffffffff89036620) (00000001) l2tp inbound (l2tp)
4: - 1fffff8 (ffffffff88879790) (00000001) Stateless verifications (in) (asm)
5: - 1fffff2 (ffffffff890586c0) (00000003) vpn tagging inbound (tagging)
6: - 1fffff0 (ffffffff89017630) (00000003) vpn decrypt verify (vpn_ver)
7: - 1000000 (ffffffff8895c0b0) (00000003) SecureXL conn sync (secxl_sync)
8: 0 (ffffffff88814ac0) (00000001) fw VM inbound (fw)
9: 10 (ffffffff8882a790) (00000001) fw accounting inbound (acct)
10: 2000000 (ffffffff89016bd0) (00000003) vpn policy inbound (vpn_pol)
11: 10000000 (ffffffff88959f40) (00000003) SecureXL inbound (secxl)
12: 21500000 (ffffffff8ad9b960) (00000001) RTM packet in (rtm)
13: 7f600000 (ffffffff8886cf30) (00000001) fw SCV inbound (scv)
14: 7f730000 (ffffffff88a8e6f0) (00000001) passive streaming (in) (pass_str)
15: 7f750000 (ffffffff88cacfb0) (00000001) TCP streaming (in) (cpas)
16: 7f800000 (ffffffff88878300) (ffffffff) IP Options Restore (in) (ipopt_res)
out chain (17):
0: -7f800000 (ffffffff88877f40) (ffffffff) IP Options Strip (out) (ipopt_strip)
1: - 1ffffff (ffffffff89015110) (00000003) vpn nat outbound (vpn_nat)
2: - 1fffff0 (ffffffff88cad1f0) (00000001) TCP streaming (out) (cpas)
3: - 1ffff50 (ffffffff88a8e6f0) (00000001) passive streaming (out) (pass_str)
4: - 1ff0000 (ffffffff890586c0) (00000003) vpn tagging outbound (tagging)
5: - 1f00000 (ffffffff88879790) (00000001) Stateless verifications (out) (asm)
6: - 1ff (ffffffff88e78d50) (00000001) NAC Packet Outbound (nac_tag)
7: 0 (ffffffff88814ac0) (00000001) fw VM outbound (fw)
8: 2000000 (ffffffff890154e0) (00000003) vpn policy outbound (vpn_pol)
9: 10000000 (ffffffff88959f40) (00000003) SecureXL outbound (secxl)
10: 1ffffff0 (ffffffff89037350) (00000001) l2tp outbound (l2tp)
11: 20000000 (ffffffff89015d80) (00000003) vpn encrypt (vpn)
12: 24000000 (ffffffff8ad9b960) (00000001) RTM packet out (rtm)
13: 60000000 (ffffffff8903e0c0) (00000001) tcpt outbound (tcp_tun)
14: 7f000000 (ffffffff8882a790) (00000001) fw accounting outbound (acct)
15: 7f700000 (ffffffff88cad3e0) (00000001) TCP streaming post VM (cpas)
16: 7f800000 (ffffffff88878300) (ffffffff) IP Options Restore (out) (ipopt_res)