- Products
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
- Partners
- More
- ABOUT CHECKMATES & FAQ
- Sign In
- Leaderboard
- Events
Call For Papers
Your Expertise, Our Stage
Ink Dragon: A Major Nation-State Campaign
March 11th @ 5pm CET / 12pm EDT
AI Security Masters E5:
Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloud
The Great Exposure Reset
AI Security Masters E4:
Introducing Cyata, Securing the Agentic AI Era
CheckMates Go:
CheckMates Fest
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Products
- :
- Hybrid Mesh
- :
- Firewall and Security Management
- :
- Re: BW Saturation
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Are you a member of CheckMates?
×
Sign in with your Check Point UserCenter/PartnerMap account to access more great content and get a chance to win some Apple AirPods! If you don't have an account, create one now for free!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Jump to solution
BW Saturation
Hello,
We have a problem with our Internet service.
We currently have a network design similar to this:
LAN -> INT_CLUSTER -> EXT_CLUSTER -> INTERNET.
The contracted BW is 500MB, but the LAN network, is having slowness problems.
The ISP told us that the link is getting saturated, and this is maybe due to a bad practice of some of the LAN users.
Is there any way to know, which is the IP that is saturating the Internet link, from the Firewall point of view?
We have ClusterXL HA in version R81.10 with Take 110.
Greetings.
BW Saturation
1 Solution
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
That's correct - if there's no entry in the heavy_conn_table, "fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn" will have nothing to display.
At this point, your best bet will be to look in either the following tabs in CPView, or collect a capture for CPMonitor:
Network -> Interfaces -> Traffic
Network -> Top-Protocols
Network -> Top-Connections
Top-Protocols and Top-Connections are not enabled by default in CPView as they can affect performance. It is best to enable them while you're trying to investigate this issue, then later disable them once finished. sk167903 contains the instructions on how to do so.
All of these assume you're viewing the gateway live at the time the incident is occurring.
25 Replies
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Buddy, what has been done so far? Have you ran any captures, checked interface errors, anything at all? Without at least basic info, it would be purely a guess as to what can be causing this.
Best regards,
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, Andy.
I checked commands like CPview, where I noticed that the Hardware resources were "stable".
I checked the command "netstat -ni", but the result of this, I did not understand it well.
This command showed a column of "RX-ERR" and the interface facing the Internet, this column did "show" a numerical value.
I suspect this may be an "indication" that there is a problem at the ISP level.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The best thing to do is see if the issue happens when you take CP firewall out of the equation. If it does, then its not the firewall, if the problem does not happen, then you know its the firewall issue and need to look further if its on the hw or software level.
Here are some commands to run.
ps -auxw
cpview (you already went through that, but you can also export it and review with command cpview -s export)
cpstat (bunch of values there for all the given blades, interfaces, etc)
ethtool command (use -S flag for specific interface...ie ethtool -S eth0)
top
free -m
fwaccel stats
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Can you post the output of netstat -ni?
This could be some sort of cabling or flow control issue.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
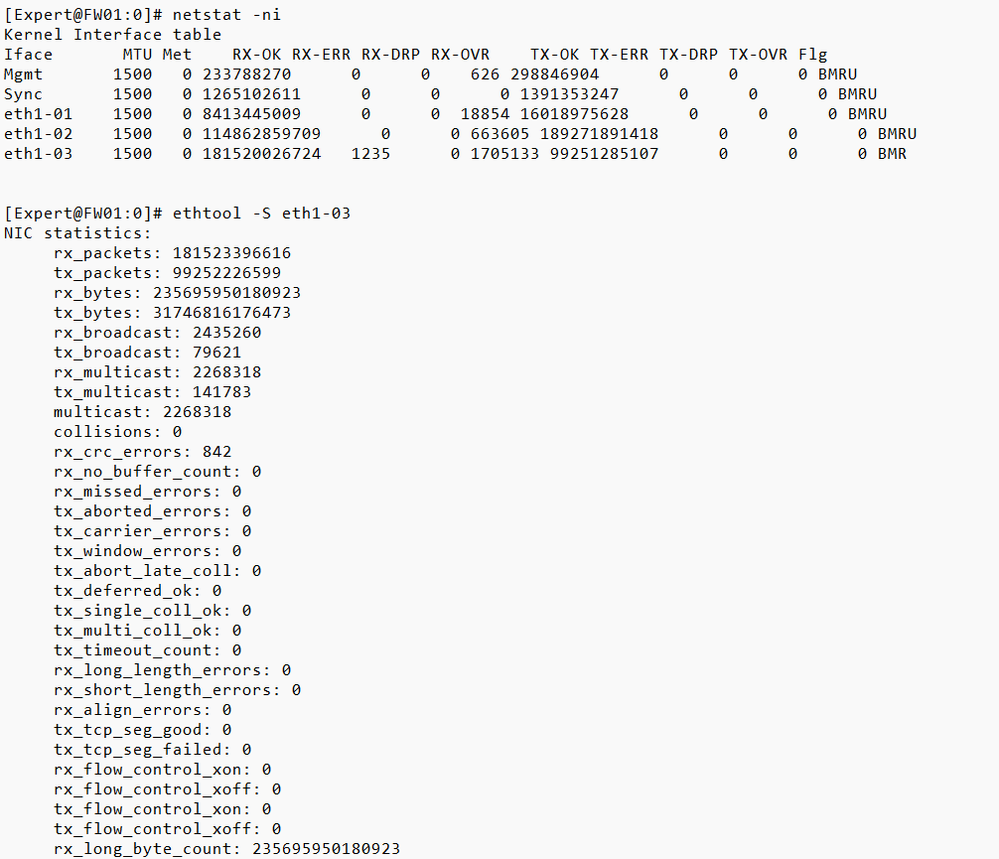
Hello,
I share the result of "netstat -ni".
From this result, what is the "important" value to take into account?
The interface that has the public IP on my GW is eth1-03.
What are the values of the commands I have shared that are "important" to consider?
Cheers.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The fact you have a non-zero RX (receive) errors on the ISP interface suggest the issue is upstream of the firewall.
The fact you're got a lot of CRC errors suggest a cabling issue of some sort.
Receive errors result in retransmissions, which will definitely impact overall performance.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
CRC errors would 100% indicate some sort of cabling problem. Check out below.
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
eth1-03 does have a few CRC errors (usually a cabling problem but the number is really low) but also has a crapload of RX-OVR indicating an overrun of inbound frames into the NIC card itself resulting in packet loss. You need to use an interface with a faster line speed there, or create an Active-Active bond of multiple interfaces. Just be sure to set the Transmit Hash Policy to L3+4 on both sides of the bond to help ensure roughly equal distribution of traffic between the physical interfaces of the bond.
The easiest way to see the bandwidth hogs is take a look at the elephant/heavy flows the firewall detected in the last 24 hours with the fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn command. top_conns will also give you the live list of top connections consuming resources through the firewall.
New Book: "Max Power 2026" Coming Soon
Check Point Firewall Performance Optimization
Check Point Firewall Performance Optimization
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
I have tried the command "fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn" on my GWs, but I have no result.
[Expert@GW01:0]# fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn
[Expert@GW01:0]#
[Expert@GW01:0]#
Do I have to install something in particular?
Greetings.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
No that just means no elephant flows were detected, try top_conns.
New Book: "Max Power 2026" Coming Soon
Check Point Firewall Performance Optimization
Check Point Firewall Performance Optimization
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
if you have no entries in the heavy_conn_table kernel table (fw tab -t heavy_conn_table -s), no output is expected from this command.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
I got this result with the command you have shared.
I understand, that not having any result, I can't have a result either, in the command that Timothy shared, right?
[Expert@GW01:0]# fw tab -t heavy_conn_table -s
HOST NAME ID #VALS #PEAK #SLINKS
localhost heavy_conn_table 16 0 0 0 0 0
Cheers.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
That's correct - if there's no entry in the heavy_conn_table, "fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn" will have nothing to display.
At this point, your best bet will be to look in either the following tabs in CPView, or collect a capture for CPMonitor:
Network -> Interfaces -> Traffic
Network -> Top-Protocols
Network -> Top-Connections
Top-Protocols and Top-Connections are not enabled by default in CPView as they can affect performance. It is best to enable them while you're trying to investigate this issue, then later disable them once finished. sk167903 contains the instructions on how to do so.
All of these assume you're viewing the gateway live at the time the incident is occurring.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
Is there any way to detect which applications, web sites, or traffic flows are consuming the most BANDWIDTH from the perspective of a ClusterXL HA?
We have increased the BW with the ISP from 1Gbps to 2Gbps, but we still have the problem of "saturation", since even with 2Gbps, the link is being saturated, and it is "terrible" that this happens.
We want to detect what exactly is "eating" all the BW.
Any recommendations please?
These are the blades I have enabled.
[Expert@FW:0]# enabled_blades
fw vpn cvpn urlf av appi ips identityServer SSL_INSPECT anti_bot mon
Cheers.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Matlu ,
How have we identified that the ISP uplink is being saturated?
Assuming that it is traffic related, analyzing the output of CPView is where you should begin investigating this. Your best bet will be to first look at the "Overview" section of the output of "cpview" while the issue is presenting itself. The "CPU" section will tell you if any of your CPUs are being heavily/fully utilized during the issue. The "Network" section is the other area you want to focus your attention, but you'll need to pay attention to this section both during the issue and outside of it in order to understand whether there's an anomalous amount of bits/packets/connections per second occurring.
If any of the parameters under CPU or Network show anomalous values, proceed to looking at the following sections if CPView:
Network -> Interfaces -> Traffic
Network -> Top-Protocols
Network -> Top-Connections
CPU -> Top-Protocols
CPU -> Top-Connections
The first will tell you whether your firewall is passing enough traffic over its interfaces to "saturate" your ISP uplink.
The second will tell you which services/ports are the most utilized by that traffic.
The third will tell you which individual connections are passing the most traffic.
The fourth and fifth, for CPU, show the same statistics as the network tab, but measured by the load they place on the CPU instead of the raw quantities.
Options #2 and #3 are not enabled by default, as they can be performance-impacting. To enable them, follow sk167903.
These should give you enough information to identify whether the issue stems from a CPU/performance issue, or a flood of traffic (or some combination of both).
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
We have been collecting the "cpview -s" and have been checking it through Grafana, and at certain periods of time, we have observed, that the external interface that gives the "face to the Internet", is "saturating".
Initially, we had a contracted BANDWIDTH of 1Gbps, but due to the urgency to solve the problem, the client decided to increase the BANDWIDTH to 2Gbps, but today, even so, we are still "feeling" BW saturations, and this causes bad browsing experience to the client's network.
So, the intention is to have a clearer idea of "why" the BW is saturating.
We believe that it could be a particular flow, or the punctual consumption of certain applications that may be "devouring" the BW.
The command "fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn" sometimes prints information in the CLI, but at other times, it does not show me anything.
Is this normal?
Greetings.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
In addition to what @D_Schoenberger said, see if you have any elephant flows going to and from the Internet currently and also in the last 24 hours:
fw ctl multik print_heavy_conn
New Book: "Max Power 2026" Coming Soon
Check Point Firewall Performance Optimization
Check Point Firewall Performance Optimization
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey bro,
I would take any advice from @D_Schoenberger . I worked with him many times on the case couple of years back, he is THE BEST! 👌
Cheers,
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey bro, any progress today on this? Things any better?
Cheers,
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Buddy,
At the moment, the client is reviewing with his ISP the detected problem, since they are observing that his contracted BW is being saturated intermittently.
For the moment, from Check Point's side, we are only "monitoring" that we do not observe anything unusual.
I understand that the most relevant value of the "netstat -ni" command that helps me to detect a significant error is the RX-OVR, right?
Greetings.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thats right. Just follow what @Timothy_Hall said, he knows this probably more than anyone out there.
Best regards,
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
In addition to what the others have mentioned, if you can collect a packet capture during the time of the bandwidth saturation, it is possible to analyze that capture using our CPMonitor tool to tell you what the top source/destination/services are.
Have a look at sk103212 for guidance on how to use the tool. If taking the capture on the external/ISP-facing interface of the firewall, you may want to also take (and analyze) captures on the internal interfaces as well to get a better idea of where the load is coming from.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Damon, nice to see you here mate : - )
I know its you, since I recognize your car, its same photo you had on every time we would do zoom meetings. Good old https inspection issue, haha.
Hope you are doing well. Good to know about that tool, dont believe I ever used it before.
Cheers,
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey Andy!
I figured using my Zoom profile pic would be the quickest way to be recognized here 🙂
CPMonitor comes in handy when trying to track down floods of traffic, always good to keep in your back pocket.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Good to know! I always ask TAC people when Im on the phone if they know you, because you are by far the most patient person I ever talked to : - )
Cheers,
Andy
Best,
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Andy
"Have a great day and if its not, change it"
Leaderboard
Epsum factorial non deposit quid pro quo hic escorol.
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 34 | |
| 18 | |
| 16 | |
| 13 | |
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 |
Upcoming Events
Thu 12 Mar 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 5: Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloudTue 17 Mar 2026 @ 03:00 PM (CET)
From SASE to Hybrid Mesh: Securing Enterprise AI at Scale - EMEAThu 12 Mar 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 5: Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloudTue 17 Mar 2026 @ 03:00 PM (CET)
From SASE to Hybrid Mesh: Securing Enterprise AI at Scale - EMEATue 17 Mar 2026 @ 02:00 PM (EDT)
From SASE to Hybrid Mesh: Securing Enterprise AI at Scale - AMERWed 18 Mar 2026 @ 10:00 AM (CET)
The Cloud Architects Series: An introduction to Check Point Hybrid Mesh in 2026 - In Seven LanguagesTue 24 Mar 2026 @ 06:00 PM (COT)
San Pedro Sula: Spark Firewall y AI-Powered Security ManagementThu 26 Mar 2026 @ 06:00 PM (COT)
Tegucigalpa: Spark Firewall y AI-Powered Security ManagementAbout CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2026 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter