- Products
Network & SASE IoT Protect Maestro Management OpenTelemetry/Skyline Remote Access VPN SASE SD-WAN Security Gateways SmartMove Smart-1 Cloud SMB Gateways (Spark) Threat PreventionCloud Cloud Network Security CloudMates General CloudGuard - WAF Talking Cloud Podcast Weekly ReportsSecurity Operations Events External Risk Management Incident Response Infinity AI Infinity Portal NDR Playblocks SOC XDR/XPR Threat Exposure Management
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- AI Security
- Developers & More
- Check Point Trivia
- CheckMates Toolbox
- General Topics
- Products Announcements
- Threat Prevention Blog
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
CheckMates Fest 2026
Join the Celebration!
AI Security Masters
E1: How AI is Reshaping Our World
MVP 2026: Submissions
Are Now Open!
What's New in R82.10?
Watch NowOverlap in Security Validation
Help us to understand your needs better
CheckMates Go:
Maestro Madness
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Products
- :
- Network & SASE
- :
- Management
- :
- Re: URL filtering vs Anti-Bot vs Anti-Virus
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Are you a member of CheckMates?
×
Sign in with your Check Point UserCenter/PartnerMap account to access more great content and get a chance to win some Apple AirPods! If you don't have an account, create one now for free!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
URL filtering vs Anti-Bot vs Anti-Virus
Hello,
Hope you are doing good.
We are just wondering, why there are loads of sites detected by URL filtering as botnets or Spyware/Malicious sites
but those are not prevented by active Anti-Bot or Anti-Virus blade.
Thanks,
Juraj
16 Replies
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
What is your exact question ? Three blades with three different fields of work, see the details for two in Threat Prevention Administration Guide R80.30 :
The Anti-Bot Software Blade uses these procedures to identify bot infected computers:
• Identify the C&C addresses used by criminals to control bots
These web sites are constantly changing and new sites are added on an hourly basis. Bots can attempt to connect to thousands of potentially dangerous sites. It is a challenge to know which sites are legitimate and which are not.
• Identify the communication patterns used by each botnet family
These communication fingerprints are different for each family and can be used to identify a botnet family. Research is done for each botnet family to identify the unique language that it uses. There are thousands of existing different botnet families and new ones are constantly emerging.
• Identify bot behavior
Identify specified actions for a bot such as, when the computer sends spam or participates in DoS attacks.
After the discovery of bot infected machines, the Anti-Bot Software Blade blocks outbound communication to C&C sites based on the Rule Base. This neutralizes the threat and makes sure that no sensitive information is sent out.
The Anti-Virus Software Blade:
• Identifies malware in the organization using the ThreatSpect engine and ThreatCloud repository:
• Prevents malware infections from incoming malicious files types (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, etc.) in real-time. Incoming files are classified on the gateway and the result is then sent to the ThreatCloud repository for comparison against known malicious files, with almost no impact on performance.
• Prevents malware download from the internet by preventing access to sites that are known to be connected to malware. Accessed URLs are checked by the gateway caching mechanisms or sent to the ThreatCloud repository to determine if they are permissible or not. If not, the attempt is stopped before any damage can take place.
• Uses the ThreatCloud repository to receive binary signature updates and query the repository for URL reputation and Anti-Virus classification.
In Security Management Administration Guide R80.30 Application Control and URL Filtering is explained as part of Access Control Policy:
Create and manage the Policy for Application Control and URL Filtering in the Access Control Policy, in the Access Control view of SmartConsole. Application Control and URL Filtering rules define which users can use specified applications and sites from within your organization and what application and site usage is recorded in the logs.
To learn which applications and categories have a high risk, look through the Application Wiki in the Access Tools part of the Security Policies view. Find ideas for applications and categories to include in your Policy.
CCSP - CCSE / CCTE / CTPS / CCME / CCSM Elite / SMB Specialist
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
question is why those sites are not being picked up by Anti-Bot blade.
Basically I would not expect to see that infected machine made a successful connection to the malware/botnet site.
I would like to see it prevented by Anti-Bot blade.
For now I can see loads sites picked up by URL filtering blade and marked as malicious/botnet
All those logs are indicating that connection was successfully made.
Whilst Anti-Bot blade is working just fine. We can see some malicious/botnets prevented by Anti-Bot blade.
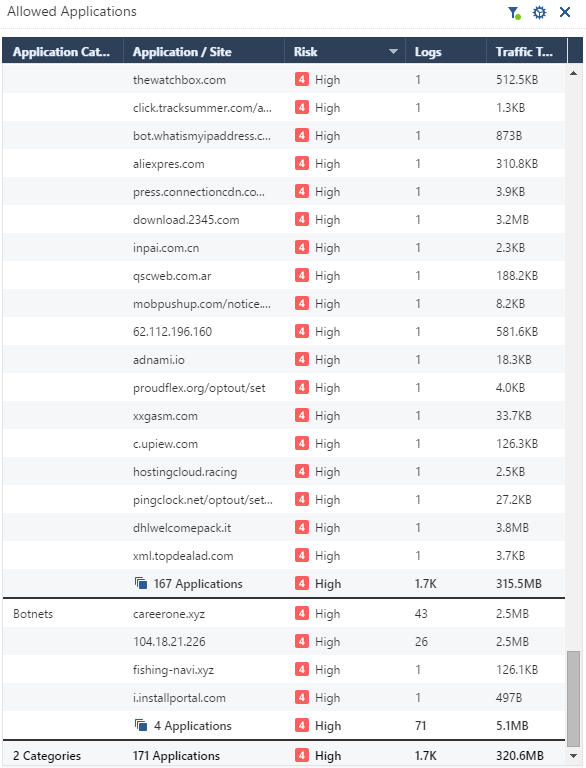
Below is just an example. There are more than 170 of them of this kind.
Thanks,
Juraj
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If you have an APCL/URLF rule that prevents access to this site category, you should involve TAC as it does not work as it should ! Preventing access to known malware URLs in done in access control policy, before ABOT can act.
CCSP - CCSE / CCTE / CTPS / CCME / CCSM Elite / SMB Specialist
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I agree.
APCL/URLF is within access control policy and only after all is good there firewall moves to Threat Prevention with ABOT.
Is this correct please?
In my case APCL/URLF is currently set in Accept action intentionally letting go all botnets and sites to see if ABOT prevents them.
And we see logs from APCL/URLF as accepted as that is the result of first access control layer and the same session is now going through second Threat Prevention layer preventing this session at the end by ABOT?
Thanks,
Juraj
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
--> In my case APCL/URLF is currently set in Accept action intentionally letting go all botnets and sites to see if ABOT prevents them.
That makes no sense at all... ABOT works if you have an unknown bot at site on a client PC - but it will not prevent connecting to known malware URL as this is done by URLF blade.
CCSP - CCSE / CCTE / CTPS / CCME / CCSM Elite / SMB Specialist
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
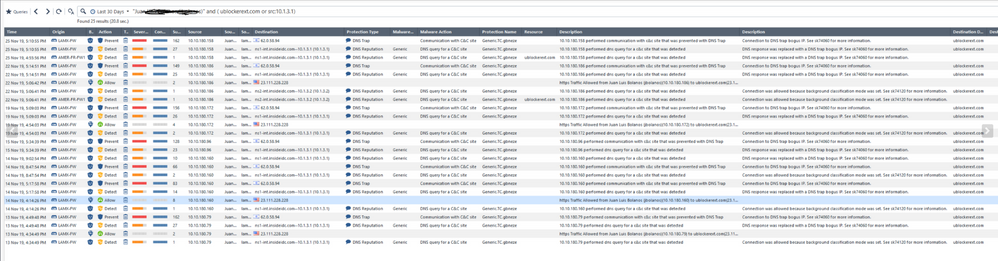
I mean basically what is shown on the printscreen
domain in this example is being recognized by both blades URLF and ABOT as Spyware/Malicious
We see accept action next to URLF and detect/prevent in ABOT
I just could not understand why we see the traffic allowed by URLF and at the same time blocked by DNS Trap.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I would suggest to contact TAC to get at the bottom of this...
CCSP - CCSE / CCTE / CTPS / CCME / CCSM Elite / SMB Specialist
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
OK thank you anyway!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi
Do you have the blades configured in hold mode or background for these tests?
CCSM R77/R80/ELITE
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
its configured for background classification. Which is fine as "hold mode" would introduce delays in domain resolutions.
Thanks,
Juraj
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Please review the log detail closely as aligned to sk74120: Why Anti-Bot and Anti-Virus connections may be allowed even in Prevent mode
CCSM R77/R80/ELITE
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
thank you for your concern.
DNS Trap functionality is clear. What was not clear is why the same session being prevented by DNS Trap was detected by URLF as successful connection to the C&C site.
As far as I understood above suggestion the reason for this is because packets are being inspected by access control policy first (Including URLF) and only after then inspection goes to the Threat Prevention (ABOT)
Implicitly I tried to conclude that packets were dropped by ABOT at the end although the packets were allowed by URLF in the first place. URLF is at the moment accepting everything for monitoring purposes.
Not sure if above makes sense or not...
Thanks,
Juraj
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Unfortunately I can't clearly make out the log screenshot on my mobile device atm, a possible explanation that can be verified with TAC may relate to the position of the DNS server that clients are performing lookups against relative to the gateway.
CCSM R77/R80/ELITE
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Please make the situation more clear: Do any of your clients have a BOT on the PC or are you talking about opening a connection to a malware site by purpose ? The later will not trigger ABOT - if URLF is disabled, connection will of course be accepted. I assume that ABOT is all about Bot behavior - when a new C&C site is found by ABOT, CP cloud will be updated and URLF will then prevent any connection.
CCSP - CCSE / CCTE / CTPS / CCME / CCSM Elite / SMB Specialist
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The simple answer is different databases are being used for AV/AB versus URL Filtering.
Which, if you think about, makes sense when you consider the primary purpose of URL Filtering, which is categorizing sites so you can decide to allow/block access to it.
Which is precisely what you should be doing in your Access Policy to sites that are deemed Botnets and Spyware/Malicious Sites.
If you're looking to test AV/AB, see: https://community.checkpoint.com/t5/IPS-Anti-Virus-Anti-Bot-Anti/How-do-I-test-if-Anti-Bot-and-or-An...
If you can provide specific examples of things you feel should be blocked in AV/AB, please send me a PM with details.
Which, if you think about, makes sense when you consider the primary purpose of URL Filtering, which is categorizing sites so you can decide to allow/block access to it.
Which is precisely what you should be doing in your Access Policy to sites that are deemed Botnets and Spyware/Malicious Sites.
If you're looking to test AV/AB, see: https://community.checkpoint.com/t5/IPS-Anti-Virus-Anti-Bot-Anti/How-do-I-test-if-Anti-Bot-and-or-An...
If you can provide specific examples of things you feel should be blocked in AV/AB, please send me a PM with details.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
yes you are correct.
Thanks for an explanation.
What got confused me is that why URLF is doing what I would call Threat Prevention (blocking botnets etc...)
URLF and ABOT have probably overlapping coverage when it comes to for example blocking malicious sites but they do it on their own.
I see it as even stronger security reinforcement.
I like it.
Thanks and regards,
Juraj
Leaderboard
Epsum factorial non deposit quid pro quo hic escorol.
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 22 | |
| 15 | |
| 8 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |
Upcoming Events
Thu 08 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 1: How AI is Reshaping Our WorldThu 22 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 2: Hacking with AI: The Dark Side of InnovationThu 12 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 3: Exposing AI Vulnerabilities: CP<R> Latest Security FindingsThu 26 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 4: Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloudThu 08 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 1: How AI is Reshaping Our WorldThu 22 Jan 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 2: Hacking with AI: The Dark Side of InnovationThu 26 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 4: Powering Prevention: The AI Driving Check Point’s ThreatCloudAbout CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter