Since R80.X much changed in the way the logging is handled and I see the subject popping-up either on its own or in other tangentially-related threads.
Changes from R77.30:
Notably absent the feature that was much welcomed, but short lived that allowed output of security events from the gateway to syslog server directly (sk87560).
*There is now a hotfix available, but it must be requested from CP support referencing Issue ID 02646044. Long term prospects for this solution are unknown.
Temporary supplement to address the lack of firewall log forwarding capability called CPLog2Syslog (sk115392) was introduced, but it does not look like it is gaining traction. Instead, Check Point is now focusing on Log Exporter (sk122323).
Smart Reporter is no longer available as a separate item and has been merged with SmartEvent. It is not, strictly speaking a logging feature, but it worth mentioning it here, as there is a heavy dependency between logs and reports.
Gateways or Cluster Members: Typically configured to send logs to the external SMS, dedicated Log Server or SmartEvent Server, they do have capability of storing logs locally in addition to shipping them off. I would consider this to be a niche case, applicable in a situation where: a.) you may have bad or intermittent connectivity between the gateway or cluster and the rest of your management infrastructure and b.) your gateways or cluster members are equipped with rotating media (conventional HDDs).
Depending on legal requirements your organization is subject to, if you are resorting to this method of logging on a single gateway, it may have to be equipped with RAID array to assure survivability of the logs in the event of the single disk failure.
You may also configure either multiple concurrent, or failure-contingent logging targets on a gateways or cluster members. This will, for instance, allow you to simultaneously log to geographically distributed Log Servers or, log locally for best performance under normal conditions with failover to the remote log server.
With single SMS / Log Server in the environment your logging destination is predetermined:
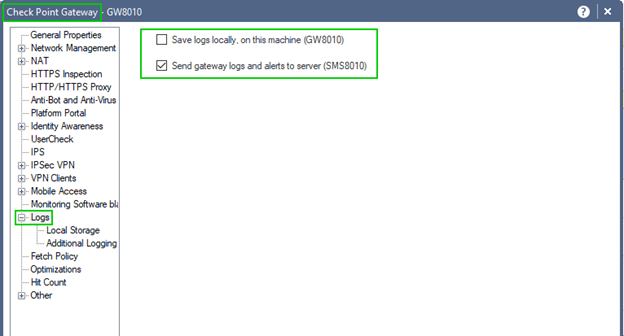
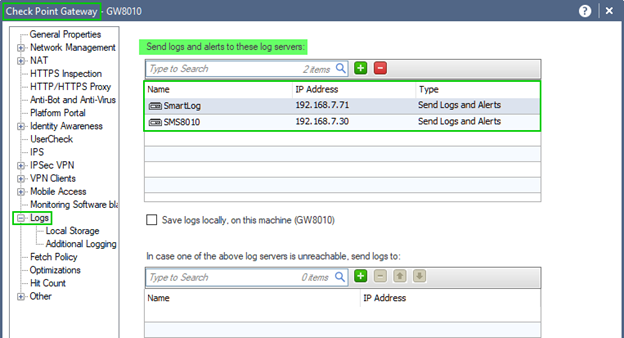
When more than one Log Server is present, your options are:
Multiple concurrent:
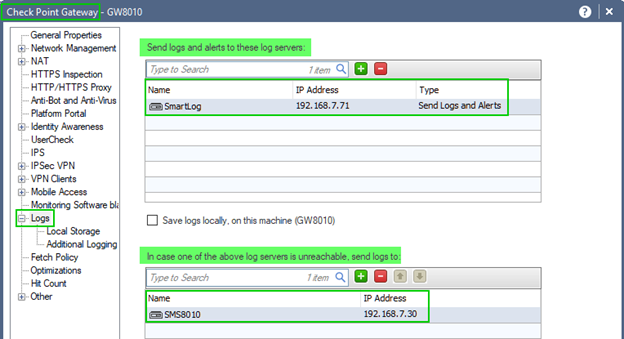
Failure Contingent:
Or a combination of both:
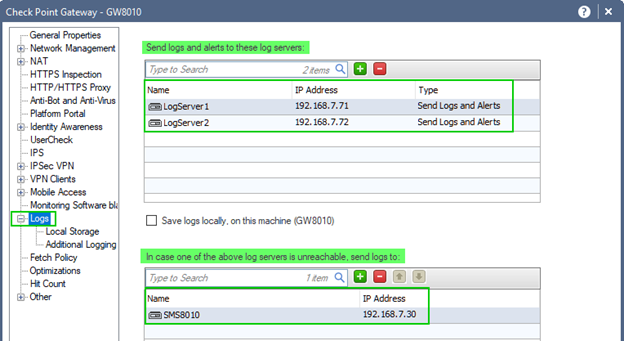
While option to "Save logs locally, on this machine (Gateway's name)" is present, it is seldom used.
Single SMS: simple enough if your logging rate or volume is not chocking the appliance or VM it is running on. All aspects of it, i.e. Logging and Status, SmartEvent and SmartEvent Correlation Unit could be configured on the same system with the "Log Indexing" enabled.
Logs are rotated at least once a day by default or more frequently, as could be specified in the host's properties/Logs/Additional Logging/Log Files section:
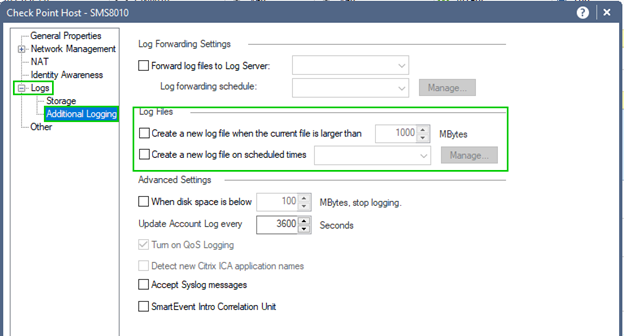
Timothy Hall adding that: log files will be forcibly rotated when they reach 2GB in size even if no log rotation checkboxes are set. I believe this is due to the old 2GB file size limit inherent in the FAT32 filesystem in Windows NT, which is an OS that very early versions of the SMS frequently used.
Running Log Indexing is limited to the last 14 days by default, but this limit could be adjusted or disabled if larger indexed time-span is desired.
By default, Log Forwarding, if enabled, will purge forwarded logs from local server, unless otherwise configured (sk106039).
No built-in archiving mechanism for the logs is available and, if required, cron scripts must be used to backup the logs for offline storage to prevent accidental overwrite.
Dedicated Log Server(s): Depending on complexity of your infrastructure, the use cases for a dedicated log server may vary. For instance, if you prefer to manage your environment from Check Point appliances that are underpowered, but otherwise sound, you may limit them to compilation and installation of policies while designating separate unit or a virtual instance with ample CPU, memory, and high-performance local or SAN-based storage array to log processing and query execution.
Alternatively, you may already have a log server(s), either standalone or in combination with management or SmartEvent components but require a near-line storage for logs that extends far beyond their capacity.
Another common use is the log consolidation across organization with multiple offices. You may have local log servers in each but are forwarding logs from all of them to a central repository.
Multiple dedicated Log Servers could be provisioned and either designated as targets for concurrent or failure-contingent logging or used for scheduled log forwarding by other components of your Check Point infrastructure.
Again, there is no built-in archiving mechanism for the logs and, if it is required, cron scripts must be used to backup the logs for offline storage to prevent accidental overwrite.
Dedicated Log Server(s) for SmartEvent: to take maximum advantage of SmartEvent's analytical capabilities, it really should have the ability to examine all traffic terminated on or traversing your gateways. This includes traffic that you may not be interested in under normal circumstances and are either allowing or dropping without logging. These are also referred to as "Complementary Logs."
To accommodate this requirement, Dedicated Log Server should be implemented. It is defined in two places: Global Properties/Reporting Tools and on each gateway or cluster.
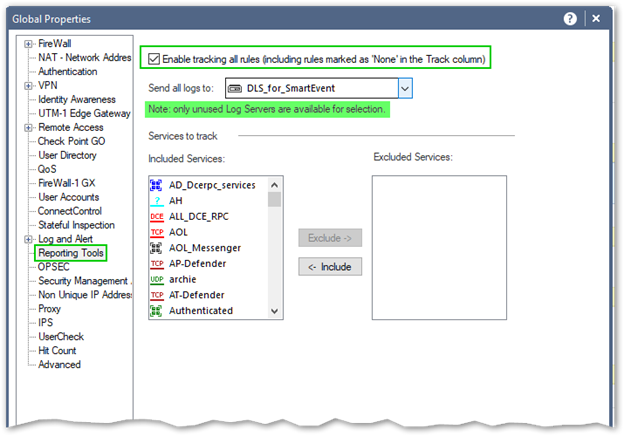
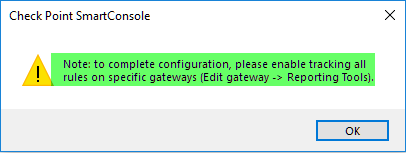
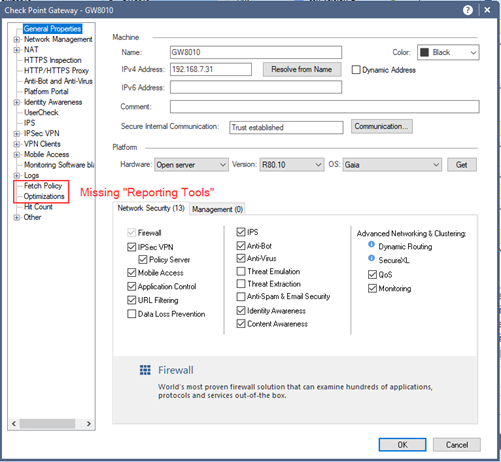
Note that “Reporting Tools” in the properties of the gateways will appear only after it is enabled in the Global Properties.
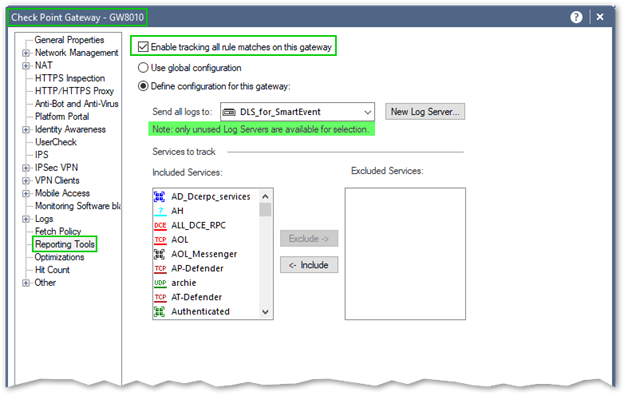
If you are simply enabling SmartEvent and SmartEvent Correlation Unit on SMS, you are NOT presented with the "Reporting Tool" options in the properties of your gateways.
Below is the screenshot of the SMS with SmartEvent and SmartEvent Correlation Unit enabled:
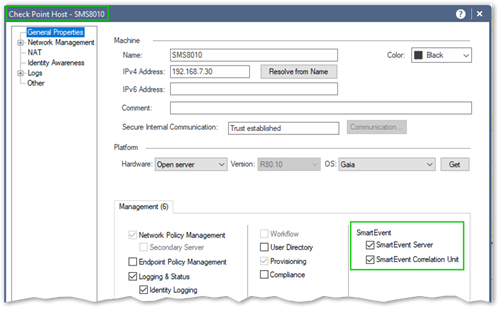
But the "Reporting Tools" option is absent:
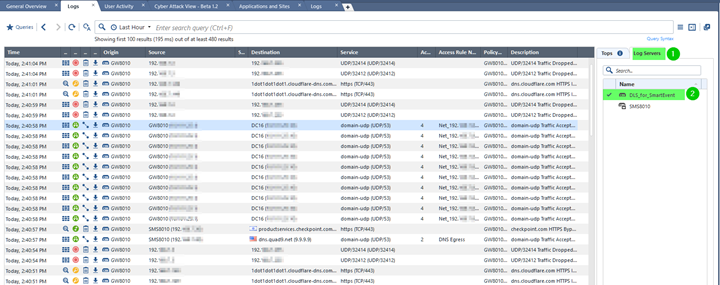
To get an idea of what is being logged by the server designated in “Reporting Tools”, select it as the only source of the events in the “Logs” tab:
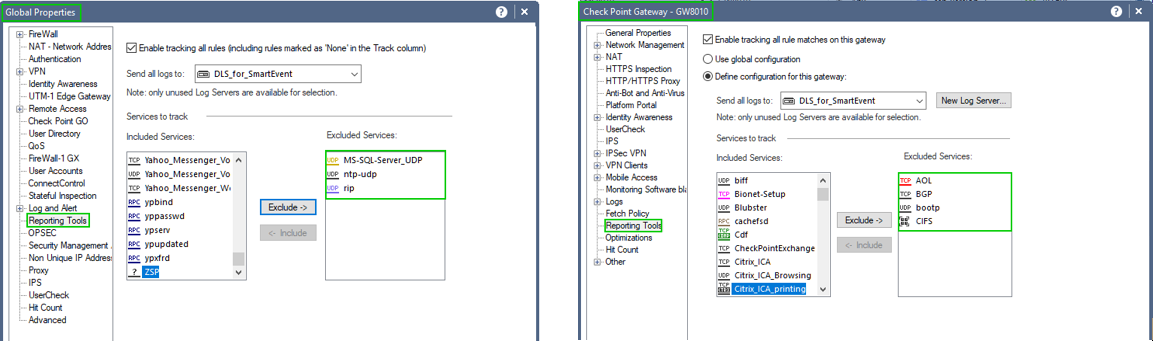
To keep the nonsense traffic from being logged by the server defined in “Reporting Tools”, add it to the “Exemptions” either in “Global Properties” or in the properties of individual gateways (clusters):
Do NOT assume that by configuring “Reporting Tools” log server you will automatically retain and have access to logs for all events! Searches by the rules with logging not enabled, by rule UUID do not return anything:
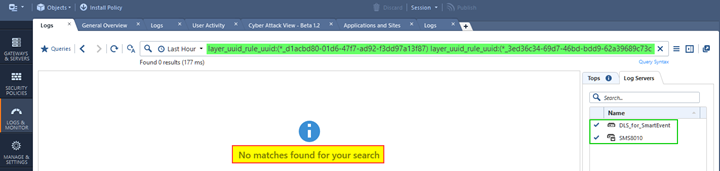
And search by source, destination and service or port number may show the only “security events of interest:”
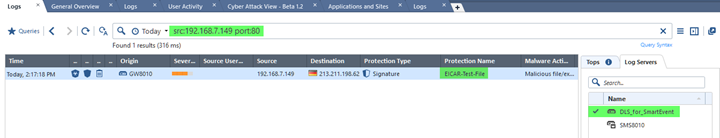
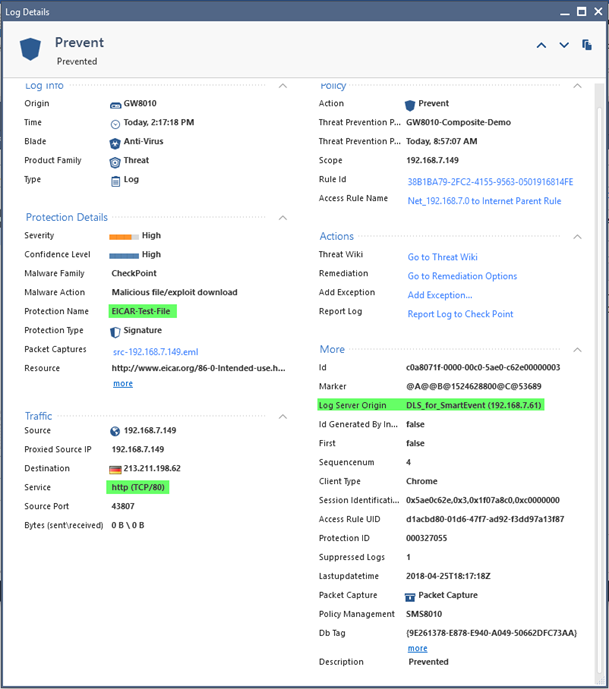
This behavior is difficult to explain, since the actual log files on the server defined in “Reporting Tools” do contain roughly same logs as the normal log servers in addition to specific additional data. We can see that by looking at the log size on both:
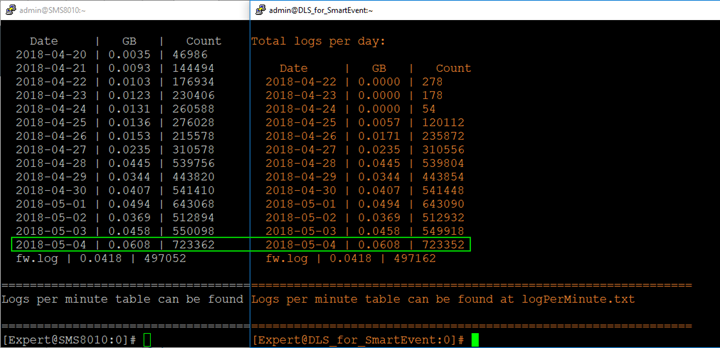
SMS HA: Used when uninterrupted management capabilities are required. Frequently implemented at a primary and secondary locations (datacenters). By default, even when blades are selected in the property of the Secondary SMS, logging to it is not automatically enabled on gateways and clusters and logs are NOT replicated:
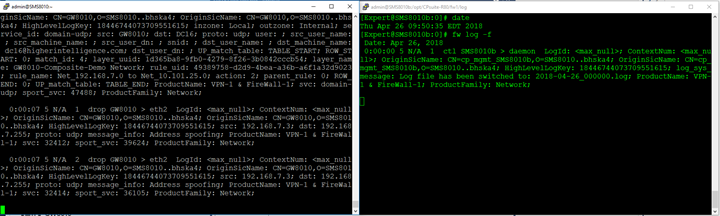
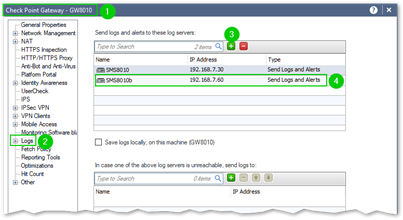
You must add Secondary SMS to the concurrent logging targets on all the gateways and clusters to retain access to the logs in case of the loss of Primary server:
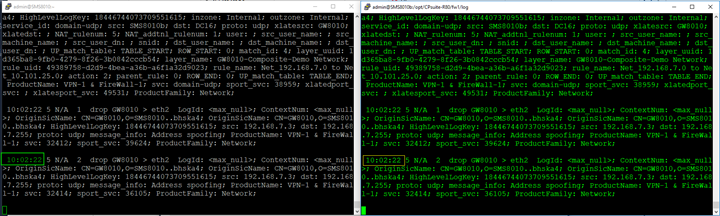
Once it is done, and the policy is installed, you are logging to both SMS’ synchronously:
...Perhaps to be continued after your comments and feedback.
Vladimir Yakovlev





















