- Products
Network & SASE IoT Protect Maestro Management OpenTelemetry/Skyline Remote Access VPN SASE SD-WAN Security Gateways SmartMove Smart-1 Cloud SMB Gateways (Spark) Threat PreventionCloud Cloud Network Security CloudMates General CloudGuard - WAF Talking Cloud Podcast Weekly ReportsSecurity Operations Events External Risk Management Incident Response Infinity Portal NDR Playblocks SOC XDR/XPR Threat Exposure Management
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- AI Security
- Developers & More
- Check Point Trivia
- CheckMates Toolbox
- General Topics
- Products Announcements
- Threat Prevention Blog
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
The Great Exposure Reset
24 February 2026 @ 5pm CET / 11am EST
CheckMates Fest 2026
Watch Now!AI Security Masters
Hacking with AI: The Dark Side of Innovation
CheckMates Go:
CheckMates Fest
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Products
- :
- General Topics
- :
- Re: R80.x Performance Tuning Tip – SMT (Hyper Thre...
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Are you a member of CheckMates?
×
Sign in with your Check Point UserCenter/PartnerMap account to access more great content and get a chance to win some Apple AirPods! If you don't have an account, create one now for free!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
R80.x Performance Tuning Tip – SMT (Hyper Threading)
| SMT (Hyper Threading) |
|---|

Hyper Threading Technology is a form of Simultaneous Multithreading Technology (SMT) introduced by Intel. Architecturally, a processor with Hyper-Threading technology consists of two logical processors per core, each of which has its own processor architectural state.Each logical processor can be individually halted, interrupted or directed to execute a specified thread, independently from the other logical processor sharing the same physical core. Unlike a traditional dual-processor configuration that uses two separate physical processors, the logical processors in a hyper-threaded core share the execution resources. These resources include the execution engine, caches, and system bus interface; the sharing of resources allows two logical processors to work with each other more efficiently, and allows a logical processor to borrow resources from a stalled logical core (assuming both logical cores are associated with the same physical core).
A processor stalls when it is waiting for data it has sent for so it can finish processing the present thread. The degree of benefit seen when using a hyper-threaded or multi core processor depends on the needs of the software, and how well it and the firewall.
Hyper-Threading works by duplicating certain sections of the processor - those that store the architectural state - but not duplicating the main execution resources. This allows a hyper-threading processor to appear as the usual "physical" processor and an extra "logical" processor to the firewall.
The number of concurrent threads can be decided by the chip designers. Two concurrent threads per CPU core are common. Because it is really an efficiency technique that inevitably increases conflict on shared resources, measuring or agreeing on its effectiveness can be difficult.
| Chapter |
|---|
More interesting articles:
- R80.x Architecture and Performance Tuning - Link Collection
- Article list (Heiko Ankenbrand)
| Preview to Intel Architecture |
|---|
The following statement is also often discussed on the Internet:
SMT can increase message rate for multi process applications by having more logical cores. This increases the latency of a single process due to lower frequency of a single logical core when hyper-threading is enabled. This means interrupt processing of the NICs will be slower, load will be higher and packet rate will decrease. I think that's why Check Point doesn't recommend SMT in pure firewall and VPN mode. From my point of view, it only accelerates software balades. Therefore I use it if necessary, if many blades are activated. I'd like to discuss that with Check Point.
Small example with basic viewing:
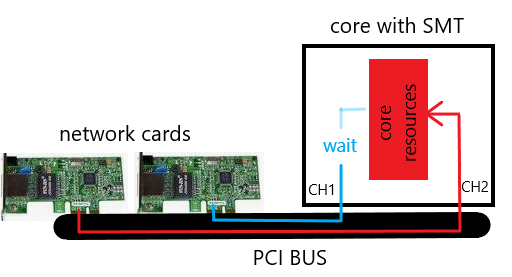
This presentation is very simplified and should illustrate the issues. If SMT channel 2 uses all core resources with I/O operations, channel 1 must wait for the core resources. This can reduce the performance with enabled SMT. The same effect can occur with multi-queue and enabled SMT. The problem can be fixed by adjusting the Check Point affinity or disable SMT. What we see here, many Intel architecture issues can affect SMT and therefore the firewall performance.
| Check Point and SMT |
|---|
SMT is a feature that is supported on Check Point appliances running Gaia OS. When enabled, SMT doubles the number of logical CPUs on the security gateway, which enhances physical processor utilization. When SMT is disabled, the number of logical CPUs equals the number of physical cores. SMT improves performance up to 30% on software blades such as IPS, Application & URL Filtering and Threat Prevention by increasing the number of CoreXL FW instances based on the number of logical CPUs.
Turning on SMT can have some side effects in terms of multi-queue and affinity. After turning on SMT the affinity should normally be adjusted.
There are also some cases in which SMT should not be used:
- if only firewall/VPN blades are used
- if these blades are enabled:
- DLP
- Anti Virus
- if these features are enabled
- Using services with resources in firewall policy
- use hide NAT extensively -> Refer to sk88160 - Dynamic NAT port allocation feature to mitigate this limitation.
- more see SK93000
Following information must also be observed before turning on SMT:
- Changing SMT state requires reboot.
- For supported appliance refer to "Supported Appliances".
- If you have two ports on any of the aforementioned appliances to handle most of the traffic, it is recommended to enable the multi-queue feature to increase SMT performance.
- For R77.30 versions only!
If the VPN blade is enabled and a significant amount of IPSec VPN traffic passes through the security gateway, then follow the steps in SK93000. - For the best performance, it is recommended that user space processes not be affined to the same physical CPU core as the secure network distributors (SNDs), but rather that they be
affined to the firewall workers CPUs (more see SK93000, SK98737). - If necessary, the affine has to be adjusted here (more see SK93000).
- Enabling SMT will load additional CoreXL FW instances. These instances consume memory and the maximal connection capacity may decrease by up to 10%.
(info from Check Point Ofir S. ) - more limitations see SK93000
Supported configurations for SMT:
- only on Check Point appliances
- only on security gateways running Gaia OS with 64-bit kernel
- supported for R77 release and later
- SMT (HT) on open servers beginning from R80.40 with kernel 3.10
(Reference : Does R80.40 support HP DL380 G10)
New with 3.10 kernel (R80.20, R80.30, R80.40):
With new kernel 3.10 for R80.20 ,R80.30 and R80.40 Check Point aligned with the industry and now HT is set and controlled by the BIOS. Therefore R80.20 and above Security Management, R80.20 and above Security Gateway with 3.10 kernel and next versions will have SMT on by default provided that the BIOS has it enabled.
Tip!
On some open servers SMT (HT) must be disabled in the BIOS for the gateway installation. This is documented in the HCL for Server see link HCL.
For example for "HP ProLitan DL360 Gen9" refert to SK Required steps before installing Gaia OS on HP ProLiant Gen9 servers.
| Supported Appliances |
|---|
Attention!
SMT is supported only on following Check Point appliances not on Open Server R80.10 - R80.30. SMT on open servers beginning from R80.40 with kernel 3.10.
| Appliance | Comment |
|---|---|
|
3100 3200 |
No hardware support for SMT. |
|
5100 5200 5400 5600 |
No hardware support for SMT. |
| 5800 5900 |
Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. SMT is recommended with all blades.
|
| 12400 | Requires 8 GB of RAM. Refer to these solutions:
cpconfig' (refer to "Enable SMT" section). |
| 12600 | Requires enabling of SMT feature both in the BIOS (1) and in 'cpconfig' (refer to "Enable SMT" section). |
| 13500 13800 |
Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. Requires enabling of SMT feature only in 'cpconfig' (refer to "Enable SMT" section). |
| 15400 15600 |
Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. SMT is recommended with all blades.
|
| 21400 21600 21700 |
SAM Acceleration card is not supported with SMT Requires enabling of SMT feature both in the BIOS (1) and in 'cpconfig' (refer to "Enable SMT" section). |
| 21800 |
Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. Requires enabling of SMT feature only in 'cpconfig' (refer to "Enable SMT" section). |
| 23500 23800 |
Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. SMT is recommended with all blades.
|
| 23900 |
Hyper Threading is hard-coded to be disabled on R77.30 and R80.10, with no impact on performance |
| TE250X TE1000X TE2000X |
Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. Requires enabling of SMT feature only in ' On these appliances, SMT is recommended with all blades. |
|
40K 60K |
SGM220 no SMT support SGM200T no SMT support SGM260 SMT support (20 physical cores / 40 with enabled SMT) SGM400 SMT support (28 physical cores / 56 with enabled SMT) |
(1) Note: To enable SMT in the BIOS, contact Check Point Support or contact Check Point Professional Services to get confirmation and approval beforehand.
| Check if SMT is activated |
|---|
Check if SMT is activated and check current SMT status on security gateway:
# cat /proc/smt_status
Either SMT is not supported on this machine or SMT is disabled in the BIOS.
![]()
SMT is enabled in the BIOS, but disabled in 'cpconfig'
![]()
SMT is enabled in BIOS and in 'cpconfig'
![]()
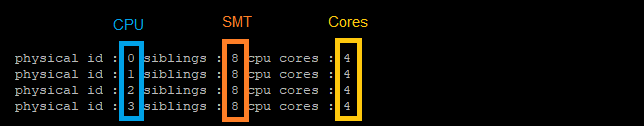
If SMT is activated this command shows the nummbers of CPUs, cores and SMTs:
# grep -E "cpu cores|siblings|physical id" /proc/cpuinfo | xargs -n 11 echo |sort |uniq
| Enable SMT |
|---|
1) Check the number of cores
# fw ctl multik stat
2) Check the number of cores in the gateway license.
# cplic print

3) Enable SMT in the BIOS + Reboot
4) Enable SMT in Check Point software and reboot the gateway.
Attention!
1) If multi-queue and affinity are not adjusted or used, this can lead to performance problems in combination with SMT.
2) Before enabling SMT, follow the instructions in SK93000 to verify that the Security Gateway can support SMT safely and check if there is enough memory available for the FW_Worker.
# cpconfig
- Choose 'Configure Hyper-Threading'
- Select 'yes'
# reboot
5) Check the number of CoreXL FW instances
# fw ctl multik stat
If the number of CoreXL FW instances did not increase automatically, then configure the CoreXL.
# cpconfig
- Choose 'Configure Check Point CoreXL'
- Set the desired number of CoreXL FW instances
(for example 3 CoreXL FW instances)
Attention!
With a ClusterXL, the core number must be the same on all gateways. Otherwise ClusterXL problems will occur.
# reboot
6) Check again the number of CoreXL FW instances
# fw ctl multik stat

| Disable SMT |
|---|
1) Disable SMT in Check Point software and reboot the gateway.
# cpconfig
- Choose 'Configure Hyper-Threading'
- Select 'No'
# reboot
2) Check the number of CoreXL FW instances
# fw ctl multik stat
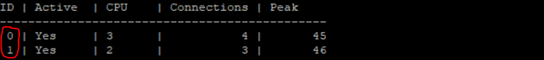
| Q&A |
|---|
Q: Which appliances were tested with SMT enabled.
A: 5800 / 5900 / 15400 / 15600 / 23500 / 23800 / TE250X / TE1000X / TE2000X
Q: I have an Open Server. Can I enable SMT in the BIOS and use it?
A: SMT is supported only on Check Point appliances.
Q: Is any degradation expected when enabling SMT?
A: Enabling SMT will load additional CoreXL FW instances. These instances consume memory and the maximal connection capacity may decrease by up to 10%.
Q: On which appliances is SMT enabled by default in the BIOS?
A: Only on 13500 / 13800 / 15400 / 15600 / 21800 / 23500 / 23800 / TE250X / TE1000X / TE2000X appliances
Q: What to do if multi-queue is enabled?
A: If using Multi-Queue, once the final CoreXL split has been set be sure to run cpmq reconfigure and reboot again, this will help ensure the new allocation of SND/IRQ cores are properly deployed for SoftIRQ processing on the Multi-Queue-enabled interfaces.
| References |
|---|
SMT (HyperThreading) Feature Guide
Best Practices - Security Gateway Performance
ATRG: CoreXL
Dynamic NAT port allocation feature
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
37 Replies
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Is SMT enabled by default on appliance?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I think yes!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yes! SMT is on appliances by default enabeld.
Felix
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Now I understatement my SMT issues.
Very fine description.
Thanks,
Kai
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
nice
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
>>> This presentation is very simplified and should >>> illustrate the issues.. If SMT channel 2 uses all >>> core resources with I/O operations, channel 1 >>> must wait for the core resources.
The support had described this to me in a similar way in a ticket.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Dear Heiko,
Nice guide , it can be better ![]()
Please allow me to ask you 3 questions :
1. What do you recommend ? Enable/Disable SMT?
2. What is the industry standard for SMT? enabled / disabled ?
3. Do you know if SMT is enabled/disabled for cloud based services/solutions ? OpenStack/VMware /IBM/AWS/Azure/Google/Alibaba/Oracle and many others ...
Some feedback:
1. SMT improve performance up to 30% for NGFW , as you wrote - more CPU's that can handle DPI.
2. Please add the data from sk93000 - you added something legacy and the SK explain exactly what is need to do
SMT (HyperThreading) Feature Guide - please add ALL data in order to make is easy , without this data I can understand otherwise.
3. About VPN - can you please point to the SK/section that explain that it's need to disable it?
sk98348 "SMT is not recommended if only FireWall/VPN blades are used" = only in case of VPN & FW
I will recommend to review sk105119 & sk104760
4. About the latency - can you please point to SK/section that explain that it's increase latency ?
Are you referring to trading traffic ? sub 5 microsecond = < 5μs = UDP only traffic ? FW only?
TCP = "Service Response Time " / "Average Round Trip" , this not the same "latency" as UDP.
Also, DPI / Proxy - add processing time , this does increase the "Service Response Time " / "Average Round Trip" as expected from any Security Device .
5. About NAT - Why NAT templates will not work ? sk71200
Thanks ,
Ofir S
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Ofir,
>>> 1. What do you recommend ? Enable/Disable SMT?
I wrote it in the article.
- On appliance SMT should always remain enabled. Except for the limitations mentioned in SK93000.
- At open server I would rather use real cores without SMT because here the hardware price not falls into the weight. Here physical cores are better in relation to the license price for CoreXL
and the performance of SMT. Since the increase in performance is only approx. 30% with SMT.
Attention! SMT is supported only on Check Point appliances not on Open Server.
I think the critical point is the network card I/O operations. If you only use the FW and VPN I tend to enable SMT. If many softwar blades are in play to SMT on.
>>> 2. What is the industry standard for SMT? enabled / disabled ?
For Windows and Linux the recommendation is to enable SMT.
>>> 3. Do you know if SMT is enabled/disabled for cloud based services/solutions?
At Cloud I have done too few projects to make a statement.
I've seen a SK here describing SMT on.
What do you say from Check Point on this topic?
---
Thank you for your answer.
I didn't want to copy the SK, so I inserted references.
I look at the other points and adjust the article if necessary.
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks a lot ![]()
A few points :
1. 5800 / 5900 / 15400 / 15600 / 23500 / 23800 / TE250X / TE1000X / TE2000X appliances, which were tested with SMT enabled.
2. I have an Open Server. Can I enable SMT in the BIOS and use it?
A: SMT is supported only on Check Point appliances.
3. Q: Is any degradation expected when enabling SMT?
A: Enabling SMT will load additional CoreXL FW instances. These instances consume memory and the maximal connection capacity may decrease by up to 10%.
4. On which appliances is SMT enabled by default in the BIOS?
A: Only on 13500 / 13800 / 15400 / 15600 / 21800 / 23500 / 23800 / TE250X / TE1000X / TE2000X appliances
5. About VPN/FW only - interesting.. I will try on next few weeks to review it .
6. About the cloud - I do not know if AWS/Azure and etc.. enable HT on their physical servers - it's a question that I thought that you might know ![]()
7. network card I/O operations - MQ ? you will utilize multiple SXL (=CPU's)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Great article Heiko! A few notes:
1) The "don't use SMT if Hide NAT is extensively used" limitation has been solved by the Dynamic NAT Port Allocation feature described here: sk103656: Dynamic NAT port allocation feature. So as long as you are running at least R77.30 with the latest GA Jumbo HFA (or R80.10+ gateway) this is no longer a concern, as this feature will enable by default if more than 6 cores are present. This was definitely an issue in R77-R77.20 and was mentioned in the first edition of my book.
2) Traffic handled in PXL (Medium Path) and F2F (Firewall Path/slowpath) by the Firewall Worker cores tends to benefit most from SMT being enabled. The reason for this is that security inspection operations in these paths tend to block often waiting for some event to occur such as the next packet in a stream to arrive, or the results of a process space "trip" like receiving a classification from the Check Point ThreatCloud. When a block occurs, SMT allows another inspection operation that has just unblocked to hop on the same physical core to get its work done. On most modern firewalls with the typical blades enabled, the vast majority of traffic tends to congregate in PXL so SMT is definitely helpful in that regard, and enabled by default on most appliances.
3) However as noted above, SMT is not recommended on firewalls with only the Firewall and IPSec VPN blades enabled (i.e. no "deep inspection" blades such as APCL/URLF or most of Threat Prevention are in use). The SND/IRQ code is highly optimized to perform relatively simpler inspection operations at ludicrous speed, with very little blocking or "waiting around" at all. This is why the fully-accelerated SXL path on the SND/IRQ cores cannot perform passive or active streaming. As such if the majority of traffic (>50%) is being handled in the SXL path as displayed by fwaccel stats -s, under high load the two SND/IRQ instances trying to execute their rapid-fire inspection operations tend to fight each other for the underlying physical core being represented as two logical cores.
4) Always a good idea to double-check free memory on the firewall with free -m once it is initially deployed with SMT enabled, or immediately after enabling SMT for the first time. The increased number of SND/IRQ and Firewall Worker instances will most definitely consume more RAM, and if the firewall is pushed over the edge into swap space usage the performance of the firewall can be dramatically affected in a negative way.
5) Also as mentioned above after enabling SMT for the first time double-check the number of kernel instances (Firewall Workers) and adjust if necessary via cpconfig. If using Multi-Queue, once the final CoreXL split has been set be sure to run cpmq reconfigure and reboot again, this will help ensure the new allocation of SND/IRQ cores are properly deployed for SoftIRQ processing on the Multi-Queue-enabled interfaces.
6) On R80.10 and earlier as each new SND/IRQ core is added, there is a roughly linear increase in overall performance for SXL path processing and SoftIRQ processing. However once more than 6 SND/IRQ cores are allocated (which is much more likely to happen with SMT enabled), the locking and coordination overhead between all the different SND/IRQ instances starts to exact a slight toll and the performance increase is no longer quite as linear as each additional SND/IRQ core is allocated beyond 6 (which is due to there only being one instance of the sim driver in the kernel, unlike the Firewall Worker cores which each have their own discrete driver instance in the kernel). Just something to be aware of, I am most definitely NOT saying that you shouldn't allocate more than six SND/IRQ cores.
All of the above is relevant to R80.10 gateway or earlier, still assessing R80.20+ gateway due to the wholesale changes in SecureXL.
--
Second Edition of my "Max Power" Firewall Book
Now Available at http://www.maxpowerfirewalls.com
Gaia 4.18 (R82) Immersion Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Video Course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Ofir,
Thanks for your support.
I like your questions and answers! I will include this in the article as Q&A.
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Ofir,
I have a question to the topic "SMT is supported only on Check Point appliances". We know that this comment been in the SK for years.
I tested with "Open Server" and SMT in lab environments and couldn't find any issues or performance disadvantages.
I would like to understand the technical background why SMT is not supported on "Open Server"?
What is the technical reason?
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Timothy,
What I find interesting about sk103656: Dynamic NAT port allocation feature is the statement:
CUT from sk103656>>>
Notes about SecureXL:
- Since R80.20 SecureXL does not have a separate port pool, and does not affect the number of ports. Since R80.20 all templates start in the Firewall.
<<<CUT
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yep not surprised, with the introduction of Column-based matching in R80.10 the need for SecureXL Accept Templates has lessened significantly.
--
Second Edition of my "Max Power" Firewall Book
Now Available at http://www.maxpowerfirewalls.com
Gaia 4.18 (R82) Immersion Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Video Course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yep, many new features in R20.20.
Joerg
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Great article !!
In addition, on 12400 / 12600 / 21400 / 21600 / 21700 appliances SMT is not activated by default in the BIOS but customer can contact Check Point support to change this : througth a remote session, the support engineer will do the activation in the BIOS (BIOS access is password-protected).
Regards,
Benoit
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello Patrik,
We enable SMT automatically since R80.10 on the Panther series (5XXX, 15XXX and 23XXX), not on the older series. For example, the SMT Status on 13500 GW will "Soft Disable" by default.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Dear Heiko,
AFAIK it's not supported for open-servers due to : you may experience installation or functionality issues later on.
sk93000 FAQ:
Q2: I have an appliance not listed in the supported appliances list. Why can't I use SMT?
A2: The SMT feature needs to be supported by both the hardware and the software. Appliances not listed do not support this feature.
sk93000 :
Supported appliance configurations:
| Appliance | Comments |
| 12400 | Requires 8 GB of RAM. Refer to these solutions:
cpconfig' (refer to "To enable SMT" section). |
| 12600 | Requires enabling of SMT feature both in the BIOS and in 'cpconfig' (refer to "To enable SMT" section). |
| 13500 13800 21800 | Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. Requires enabling of SMT feature only in 'cpconfig' (refer to "To enable SMT" section). |
| 21400 21600 21700 | SAM Acceleration card is not supported. Requires enabling of SMT feature both in the BIOS and in 'cpconfig' (refer to "To enable SMT" section). |
| 5800 5900 15400 15600 23500 23800 | Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. 5800 / 15400 / 15600 / 23500 / 23800 appliances require:
On 5800 / 5900 / 15400 / 15600 / 23500 / 23800 appliances, SMT is recommended with all blades. |
| TE250X TE1000X TE2000X | Is already shipped with enabled SMT feature in the BIOS. Requires enabling of SMT feature only in ' On these appliances, SMT is recommended with all blades. |
Note: To enable SMT in the BIOS, contact Check Point Support or contact Check Point Professional Services to get confirmation and approval beforehand.
+ sk107516 :
| On 23900 appliances, Hyper Threading is hard-coded to be disabled on R77.30 and R80.10, with no impact on performance |
+ sk93332 :
The following table shows various hardware information about SGMs:
| Criteria | SGM220 | SGM220T (for NEBS) (1) | SGM260 | SGM400 |
| CPU Cores | 8 / 12 | 8 / 12 | 20 physical / 40 with enabled Hyper Threading | 28 physical / 56 with enabled Hyper Threading |
Notes:
- SGM220T is supported only by the 61000 / 61000 N+N Security Systems.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Ofir,
thanks for the information. I think it's very nice that you support so well here in Checkmates forum.
I will include the information in the article.
Thanks,
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Why is SMT not supported on 23900 appliances (even to the point of being disabled in code)? Does that change in R80.20? Why would the Checkpoint appliance comparison chart show the 23900 having 36 physical cores and 72 virtual cores if SMT isn't allowed?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I think this is due to the CoreXL 40 core limitation in R80.10. I don't think this limit was changed in R80.20, at least that I can find.
--
Second Edition of my "Max Power" Firewall Book
Now Available at http://www.maxpowerfirewalls.com
Gaia 4.18 (R82) Immersion Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Video Course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks Timothy Hall! So, then, is the only benefit on the 23900 that you get 12 extra physical cores? A couple follow up questions:
- Performance-wise, how does the 23900 compare to the 23800 with SMT turned on, giving 48 virtual cores?
- On the 23800, if there is a 40 FW worker process limitation in CoreXL, I assume only 40 of the virtual cores would be available to CoreXL?
- Bang for buck, is the 23900 worth it over the 23800 based on these limitations?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Two physical non-hyperthreaded cores will always perform much better than two logical cores that are actually one physical core. Under ideal circumstances there would be about a 30% performance increase by having a physical core being presented as two logical cores. In the real world the gain can be slightly higher than that or lower (even much lower) depending on a wide variety of factors such as workload characteristics.
It is a bit difficult to generalize about the exact performance of different appliances because there are more factors than just raw CPU speed at work (such as CPU fast cache amounts and main memory speed/channels which can make a huge difference). But if we just go by number of available cores the 23900 would have 36 physical cores while the 23800 would have 20*2 = 40 hyperthreaded cores. Assuming that the raw physical core processing speed between the two appliances is equal (which it probably isn't, I'd imagine the 23900 would have a more advanced processor architecture and be slightly faster per-core), the hyperthreading-adjusted value would be 36 cores for the 23800 and 26 cores for the 23800 (40*1.3). This is making a gargantuan assumption that the gains from hyperthreading would be 30% on the 23800, hence the factor of 1.3. The 23900 is about 30% more expensive than the 23800, but is about 40% faster than the 23800 with current CoreXL limitations. If the current 40-core CoreXL limitation was lifted, the 23900's hyperthreading-adjusted speed given these assumptions would be approximately 47 cores (36*1.3), or nearly twice as fast as the 23800.
The value judgement based on these admittedly broad assumptions is left as an exercise to the reader. 🙂
Edit: User Space Firewall (USFW) in R80.30 removes the 40-core limit mentioned above, so those extra processors over 40 can now be utilized.
Side Note: Has anyone done a cat /proc/cpuinfo on a 23900, what processor is it using?
--
Second Edition of my "Max Power" Firewall Book
Now Available at http://www.maxpowerfirewalls.com
Gaia 4.18 (R82) Immersion Tips, Tricks, & Best Practices Video Course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
Now Available at https://shadowpeak.com/gaia4-18-immersion-course
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Received several private mails on the topic.
Therefore again:
Do not enable HT on open server.
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks again for your support.
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yes, more see here:
https://community.checkpoint.com/thread/9676-r8020-new-interesting-commands
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Update:
- SMT (HT) on open servers beginning from R80.40 with kernel 3.10
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
Leaderboard
Epsum factorial non deposit quid pro quo hic escorol.
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 22 | |
| 21 | |
| 12 | |
| 9 | |
| 9 | |
| 8 | |
| 8 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 |
Trending Discussions
Upcoming Events
Thu 12 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 3: AI-Generated Malware - From Experimentation to Operational RealityFri 13 Feb 2026 @ 10:00 AM (CET)
CheckMates Live Netherlands - Sessie 43: Terugblik op de Check Point Sales Kick Off 2026Thu 19 Feb 2026 @ 03:00 PM (EST)
Americas Deep Dive: Check Point Management API Best PracticesThu 12 Feb 2026 @ 05:00 PM (CET)
AI Security Masters Session 3: AI-Generated Malware - From Experimentation to Operational RealityFri 13 Feb 2026 @ 10:00 AM (CET)
CheckMates Live Netherlands - Sessie 43: Terugblik op de Check Point Sales Kick Off 2026Thu 19 Feb 2026 @ 03:00 PM (EST)
Americas Deep Dive: Check Point Management API Best PracticesAbout CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2026 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter


