In today's interconnected world, the Internet of Things - IoT has emerged as a powerful force, transforming industries and enhancing the way we live and work. However, with this rapid growth in IoT devices and applications, the need for global regulations to govern this technology has become imperative.
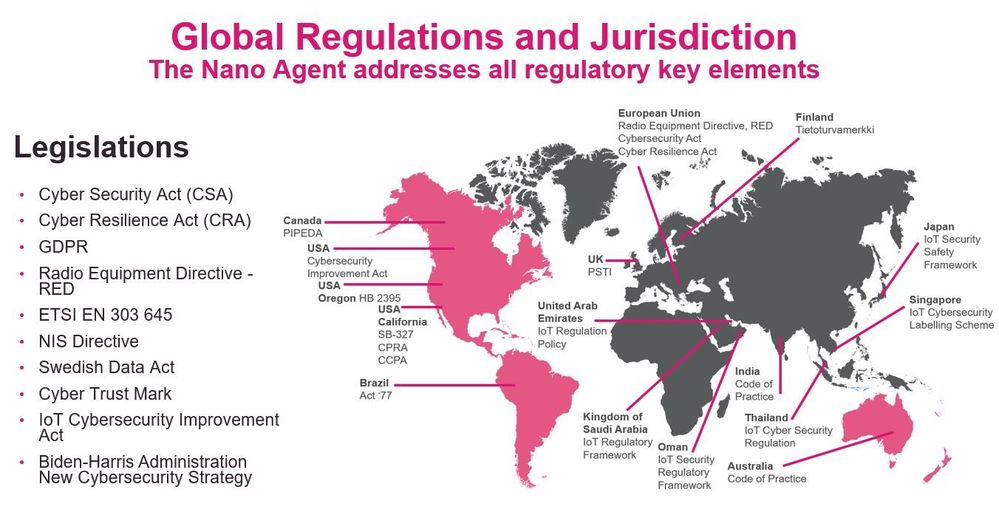
Figure 1: Overview of global IoT regulations (voluntary or mandatory)
Why do we need Global IoT Regulation
As IoT devices become more prevalent in our work and daily lives, concerns regarding data privacy, security and interoperability have become increasingly significant. Global IoT regulations aim to address these concerns and establish a framework that ensures the responsible and secure deployment of IoT technologies worldwide.
Key elements of Global IoT Regulations
1. Data Privacy and Security | Privacy is a fundamental right and protecting individuals' data or sensitive data is of utmost importance. Global IoT regulations emphasize the need for robust data protection measures, including clear consent mechanisms, secure data storage and encryption protocols. Additionally, regulations often require device manufacturers to implement security features to safeguard against cyber threats.
2. Interoperability and Standardization | With a vast array of IoT devices and platforms available, ensuring interoperability is essential for seamless communication and efficient data exchange. Global regulations encourage the adoption of open standards and protocols, promoting compatibility and interoperability among different IoT systems.
3. Ethical Considerations | As IoT technologies become more sophisticated, ethical concerns arise. Global IoT regulations may address issues such as algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation and the responsible use of AI in IoT systems. These regulations aim to ensure that IoT deployments adhere to ethical principles and do not infringe upon individual rights.
4. Spectrum Allocation and Connectivity | IoT devices rely on wireless connectivity, making spectrum allocation a critical consideration. Global regulations seek to allocate appropriate frequency bands for IoT applications while ensuring optimal spectrum management and minimizing interference with other wireless services.
5. Certification and Compliance | To ensure the adherence to established regulations, certification and compliance programs are often implemented. These programs require manufacturers to undergo testing and assessment to verify that their IoT devices and systems meet regulatory requirements. Compliance with these programs assures users that the IoT products they utilize conform to the necessary standards.
The Importance of Staying Informed
As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial for individuals and organizations to stay informed about global IoT regulations. Being aware of these regulations enables stakeholders to make informed decisions, develop IoT solutions that comply with legal requirements and mitigate potential risks associated with non-compliance.
In conclusion, global IoT regulations play a vital role in shaping the responsible and secure deployment of IoT technologies worldwide. By addressing data privacy, security, interoperability, ethical considerations, and more, these regulations provide a framework for the sustainable growth of the IoT ecosystem.




