- CheckMates
- :
- Products
- :
- CloudMates Products
- :
- Cloud Network Security
- :
- Discussion
- :
- CME and AutoUpdater
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Are you a member of CheckMates?
×- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
CME and AutoUpdater
CME background
The Cloud Management Extension (CME) is a utility that runs on Check Point Security Management Servers and Multi-Domain Security Management Servers that are deployed in a cloud or on-premises.
This utility allows integration between Check Point CloudGuard IaaS solutions and cloud platforms such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), Azure, and GCP (Google Cloud Platform).
The CME is mandatory if your deployment is a CloudGuard Network VMSS / ScaleSet / MIG.
The CME is responsible to run a periodic query against the cloud provider and check the status of the VMSS / ScaleSet / MIG.
The CME compering the gateways objects that are on the Check Point management servers to the gateways instances on the cloud provider, in case a gateway instance has been deleted from the cloud provider and still exists on the Check Point management server, The CME will delete the gateway object from the management server.
In case a gateway instance exists on the cloud provider but not on the management, the CME will add the new gateway object to the management, create a sic with it, configure it and deploy policy on the new gateway.
More about CME on SK157492
AutoUpdater Background
AutoUpdater is a Check Point process responsible for automatic updates.
The latest updates are installed automatically on all relevant Check Point servers, if the user allows the Automatic Updates Download as described in sk94508.
CME AutoUpdate
It’s important to keep the CME up to date.
CME version 108 and above support automatic updates.
In case your CME version is lower than 108, you will need to uninstall the CME package manually and deploy the latest version.
On uninstalling the package, the CME configuration will remain.
To find the CME configuration files use one of these directories:
- On a Security Management Server: $FWDIR/conf/
- On a Multi-Domain Security Management Server: $MDSDIR/conf
To check if CME is installed at all and if yes, what the CME version is, run the command from bash: cpinfo -y all | grep CME
To uninstall the older version that does not support autoupdate , you will need to find the CME package name.
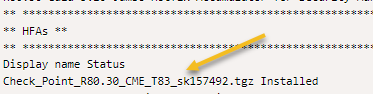
For example
And run the command on clish: installer uninstall Check_Point_R80.30_CME_T83_sk157492.tgz
You can find more info here and also How to work with CPUSE - How to uninstall a CPUSE package here
Autoupdater
If autoupdater service is running on your management server and configured to download and update component automatically , the newest CME service will be installed automatically on the next autoupdater run ( it run automatically every 3 hours)
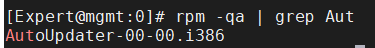
To check if there is an autoupdater on the mangment , run the command form bash :
rpm -qa | grep Aut
If autoupdater is not installed, check the instructions on sk165653
In order to check if autoupdater is enabled to CME , run the command : autoupdatercli show
If the installer scheduler is the to false, you can change it to true by running the command : autoupdatercli enable CME
Instead of waiting for 3 hours for the auto updater will start his operation, you can run the command :
autoupdatercli stop
It will automatically restart Darwin and all available packages will be downloaded and installed.
To check the autoupdater progress, check the autoupdater log with the following command:
tail -F /opt/AutoUpdater/AutoUpdater.log
If you would like to install the latest CME version manually , download the latest CME package from sk157492
And run the command autoupdatercli install /<Full Path>/<Name of Package>