- Products
Quantum
Secure the Network IoT Protect Maestro Management OpenTelemetry/Skyline Remote Access VPN SD-WAN Security Gateways SmartMove Smart-1 Cloud SMB Gateways (Spark) Threat PreventionCloudGuard CloudMates
Secure the Cloud Cloud Network Security CloudMates General CNAPP CloudGuard - WAF Talking Cloud Podcast Weekly Reports - Learn
- Local User Groups
- Partners
- More
This website uses Cookies. Click Accept to agree to our website's cookie use as described in our Privacy Policy. Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
- Products
- Learn
- Local User Groups
- Upcoming Events
- Americas
- EMEA
- Czech Republic and Slovakia
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Germany
- Sweden
- United Kingdom and Ireland
- France
- Spain
- Norway
- Ukraine
- Baltics and Finland
- Greece
- Portugal
- Austria
- Kazakhstan and CIS
- Switzerland
- Romania
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Belgium & Luxembourg
- Russia
- Poland
- Georgia
- DACH - Germany, Austria and Switzerland
- Iberia
- Africa
- Adriatics Region
- Eastern Africa
- Israel
- Nordics
- Middle East and Africa
- Balkans
- Italy
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- APAC
- Partners
- More
- ABOUT CHECKMATES & FAQ
- Sign In
- Leaderboard
- Events
Open Garden In Action:
Find and Remediate Threats Everywhere!
Introducing Check Point Quantum Spark 2500:
Smarter Security, Faster Connectivity, and Simpler MSP Management!
New Appliance Announcements
and Faster Threat Prevention
Check Point Named Leader
Forrester Wave™: Zero Trust Platforms, Q3 2025
Remote Access VPN – User Experience
Help us with the Short-Term Roadmap
CheckMates Go:
AI Agents
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- CheckMates
- :
- Products
- :
- Quantum
- :
- Security Gateways
- :
- One-liner for Address Spoofing Troubleshooting
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Are you a member of CheckMates?
×
Sign in with your Check Point UserCenter/PartnerMap account to access more great content and get a chance to win some Apple AirPods! If you don't have an account, create one now for free!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
One-liner for Address Spoofing Troubleshooting
🏆 Code Hub Contribution of the Year 2019!
📌 Available as SmartConsole Extension.
👍 Endorsed by Check Point Support!
One-liner (Bash) to show a summary about each gateway interfaces' calculated topology and address spoofing setting.
In expert mode run:
echo;tput bold;if [[ `$CPDIR/bin/cpprod_util FwIsFirewallModule 2>/dev/null` != *'1'* ]];then echo ' Not a firewall gateway!';tput sgr0;echo;elif [[ `grep $(echo -n :[[:space:]]\(;grep $(hostname)$ /etc/hosts|cut -f1 -d' ') $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set|wc -l` == "0" ]] && ([[ $INSTANCE_VSID == '0' ]] || [[ $INSTANCE_VSID == '' ]]);then echo ' Main IP of '$(hostname)' doesn`t match it`s management interface IP!';tput sgr0;echo;else echo -n ' Interface Topology ';tput sgr0;echo -n '> ';tput bold;tput setaf 1;if [[ -n "$vsname" ]] && [[ $vsname != *'unavail'* ]];then echo $vsname' (ID: '$INSTANCE_VSID')';else hostname;fi;tput sgr0;echo -n ' ';printf '%.s-' {1..80};echo;egrep -B1 $'ifindex|:ipaddr|\(\x22<[0-9]|objtype|has_addr_info|:monitor_only|:external' $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set|sed -n "/$(if [[ -n "$vsname" ]] && [[ $vsname != *'unavail'* ]] && [[ $INSTANCE_VSID != '0' ]];then echo $vsname;else grep `hostname`$ /etc/hosts|cut -f1 -d' ';fi)*$/,\$ p"|tail -n +3|sed 's/[\x22\t()<>]//g'|sed 's/--//g'|sed '$!N;s/\n:ipaddr6/ IPv6/;P;D'|sed '/IPv6/!s/://g'|sed 's/interface_topology/\tCalculated Interface Topology/g'|sed '0,/ifindex 0/{/ifindex 0/d;}'|sed '/ifindex 0/q'|sed '/spoof\|scan/d'|sed 's/has_addr_info true/\tAddress Spoofing Protection: Enabled/g'|sed 's/has_addr_info false/\tAddress Spoofing Protection: Disabled/g'|sed -e '/Prot/{n;d}'|sed '$!N;s/\nmonitor_only true/ (Detect Mode)/;P;D'|sed '$!N;s/\nmonitor_only false/ (Prevent Mode)/;P;D'|sed '$!N;s/\nexternal false/ - Internal Interface/;P;D'|sed '$!N;s/\nexternal true/ - External Interface/;P;D'|sed '/objtype/q'|tac|sed '/ifindex 0/I,+2 d'|sed '/Address/,$!d'|tac|sed '/ifindex/d'|sed 's/,/ -/g'|sed '$!N;s/\nipaddr/ >/;P;D'|sed '/ - /s/^ /\t/'|egrep -C 9999 --color=auto $'>|IPv6|External|Disabled|Detect';echo;fi![]()
The One-liner is IPv4 and IPv6 compatible, works on clustered and single gateway environments also within VSX, shows all interface types configured in your firewall object within SmartDashboad, colors specific words of the output for easier identification of important settings, adds additional information regarding Address Spoofing setting and mode as well as the topology type of each interface and is of course completely integrated within our ccc script.
Thanks to Tim Hall's preliminary work in this thread.
Thanks to Norbert Bohusch for IPv6 support and testing.
Thanks to Kaspars Zibarts, Bob Zimmerman, Jan Kleinhans for VSX support and testing.
Thanks to Anthony Joubaire for support and testing multiple installation targets.
56 Replies
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Denny,
I built something once.
Depending on the interface, the corresponding networks from the IP spoofing area are displayed.
More see in this article:
Show Address Spoofing Networks via CLI
First experiment:
ifconfig -a | grep encap | awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v bond | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq'
Second experiment:
ifconfig -a | grep encap | awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v bond | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ '
Final version:
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v bond | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ '
Output:
eth0
10.0.0.0, 10.255.255.255
192.168.1.0, 192.168.1.255
eth2
0.0.0.0, 9.255.255.255
11.0.0.0, 126.255.255.255
128.0.0.0, 192.168.41.255
192.168.202.0, 223.255.255.255
192.168.43.0, 192.168.200.255
240.0.0.0, 255.255.255.254
eth3
192.168.2.0, 192.168.2.255
eth5
10.172.1.0, 10.172.1.255
Can be formatted even better with AWK,TR,SED.
Best Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
With IP and netmask:
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v bond | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 8 %|grep ip| tr \a\d\r\:\(\) \ ;echo -n " mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo " spoofing networks:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
More see in this article:
https://community.checkpoint.com/docs/DOC-2990-show-address-spoofing-networks-via-cli
Output:
eth0 < Interface
ip 10.1.1.251 < IP
ip 10.1.1.252
mask 255.255.255.0 < Netmask
spoofing networks:
10.0.0.0, 10.255.255.255 < spoofing networks
192.168.1.0, 192.168.1.255
eth2
ip 1.1.1.211
ip 1.1.1.212
mask 255.255.255.0
spoofing networks:
0.0.0.0, 9.255.255.255
11.0.0.0, 126.255.255.255
128.0.0.0, 192.168.41.255
192.168.220.0, 223.255.255.255
192.168.4.0, 192.168.8.255
240.0.0.0, 255.255.255.254
eth3
ip 192.168.2.131
ip 192.168.2.132
mask 255.255.255.0
spoofing networks:
192.168.2.0, 192.168.2.255
eth5
ip 10.172.1.102
ip 10.172.1.103
mask 255.255.255.0
spoofing networks:
10.172.1.0, 10.172.1.255
PS:
Here two IP addresses are visible, because it is a cluster with vip.
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Sweet!
Does that meet your requirements Danny Jung?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Sir Heiko,
What is the meaning of the section of Spoofing Networks in this script? is it the Network Address detected by Check Point which is showing in the logs as Address Spoofed networks?
Hope you can give clearance on this, we have tried this script to run, and want to understand the output.
Thanks.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
This command is intended to show the current anti-spoofing configuration as configured in SmartConsole.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, Denny,
2500 points are a bit much 10 while also ok.![]()
We all like to help.
I'm going to update the CLI command a little bit this weekend. Maybe there's more you can get out of it.
I think that's very helpful. I would also like to include the routes and separate the VIP and physical IP.
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Your version contains an issue where an interface is still configured in a gateway's topology within SmartDashboard but was deleted on the GAiA OS and is therefore not shown via ifconfig. As your command relies on ifconfig this critical information is not reflected.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 8 %|grep ip| tr \a\d\r\:\(\) \ ;echo -n " mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo " spoofing networks:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
I noticed that the bond interface was not displayed in the old version. Tested it on about 5 firewalls. Everything looks good so far.
For more infos see in this article with revisions:
Show Address Spoofing Networks via CLI
-
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Command:
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;echo -n " VIP "; cphaprob -a if |grep %|grep -v U|grep -v D | cut -c16-| tr -d "\r\n" ;echo;echo -n " IP ";ifconfig % | grep "inet addr" | cut -d ":" -f 2 | cut -d " " -f 1;echo -n " Mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo " ADDRESS SPOOFING NETWORKS:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
I noticed that the vip and ip interface was not displayed in the old version.
Example:
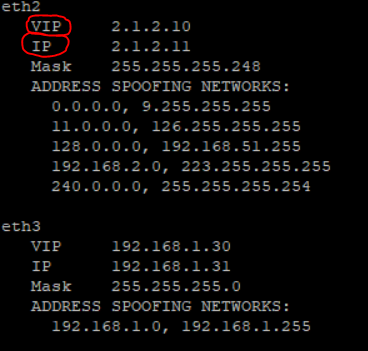
For more infos see in this article with revisions:
Show Address Spoofing Networks via CLI
-
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
And the latest version:
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;echo -n " VIP "; cphaprob -a if |grep %|grep -v U|grep -v D | cut -c16-| tr -d "\r\n" ;echo;echo -n " IP ";ifconfig % | grep "inet addr" | cut -d ":" -f 2 | cut -d " " -f 1;echo -n " Mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo -n " ANTISPOOFING ENABLED: ";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep has_addr_info | cut -c17- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq ; echo -n " DETECT=true or PREVENT=false: "; more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 "eth5" | grep monitor_only | cut -c16- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq ;echo " ADDRESS SPOOFING NETWORKS:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
Now you can see the states off:
- ANTISPOOFING ENABLED
- DETECT=true or PREVENT=false
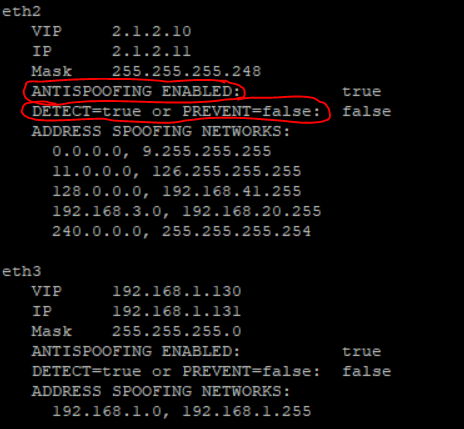
For more infos see in this article with revisions:
Show Address Spoofing Networks via CLI
Now I need a break. The one-liner make me crazy![]() .
.
Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Let's talk about some improvements.
Instead of your beginning:
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^loI'd suggest
grep -B1 ifindex $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | sed -n '1~3p' | cut -c 4- | sort | uniqinstead to actually reflect the calculated topology from SmartDashboard and not the one that is configured on GAiA OS. Otherwise users will run into issues if the configured interfaces topology in SmartDashboard doesn't match the one ifconfig results.
Furthermore I'd be of help if your One-liner would would return MODE: Detect or Mode: Prevent instead of DETECT=true or PREVENT=false.
I also noticed that your One-liner is currently grepping directly for eth5. This doesn't look correct.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello Danny,
Thanks for the 2500 points. It's a little too much for a one-liner.
I think it's a great community and we should all help each other without rewards.
I gave you back 2500 points ![]() for your great work in this article Common Check Point Commands (ccc).
for your great work in this article Common Check Point Commands (ccc).
And thanks to everyone who helped to find the great commands for ccc.
Best Regards
Heiko
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Sorry, of course a % must be used instead of eth5.
Here is the right version:
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;echo -n " VIP "; cphaprob -a if |grep %|grep -v U|grep -v D | cut -c16-| tr -d "\r\n" ;echo;echo -n " IP ";ifconfig % | grep "inet addr" | cut -d ":" -f 2 | cut -d " " -f 1;echo -n " Mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo -n " ANTISPOOFING ENABLED: ";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep has_addr_info | cut -c17- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq ; echo -n " DETECT=true or PREVENT=false: "; more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep monitor_only | cut -c16- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq ;echo " ADDRESS SPOOFING NETWORKS:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I hope this will be integrated into CCC.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
My original version is integrated within ccc starting from version 2.5.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Danny,
I think the "fw ctl zdebug drop" problem is not solvable because there is no interface mapping.
Output from "fw ctl zdebug drop":
;[cpu_1];[fw4_0];fw_log_drop_conn: Packet <dir 1, 1.1.1.2:59655 -> 2.9.2.3:53 IPP 17>, dropped by do_inbound, Reason: Address spoofing;
Regards,
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I'm checking on this if we could utilise some "after" event log fetch from log storage but that would be dependent on spoofing being logged actually. ![]() and it would not be that instantaneous
and it would not be that instantaneous ![]()
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Heiko Ankenbrand: I added to output not false/true but PREVENT/DETECT, but encountered another thing, not considered in your one-liner: VLAN Trunks (phy. IFs are also displayed and with all VLAN VIPs/Spoofing Networks)
Here the altered one-liner and a screenshot with the VLAN trunk issue:
# ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;echo -n " VIP "; cphaprob -a if |grep %|grep -v U|grep -v D | cut -c16-| tr -d "\r\n" ;echo;echo -n " IP ";ifconfig % | grep "inet addr" | cut -d ":" -f 2 | cut -d " " -f 1;echo -n " Mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo -en " ANTISPOOFING ENABLED:\t";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep has_addr_info | cut -c17- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq ; echo -en " ANTISPOOFING MODE:\t"; if [ `more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep monitor_only | cut -c16- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq` ]; then echo "PREVENT"; else echo "DETECT"; fi;echo " ADDRESS SPOOFING NETWORKS:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Nice!
Had after 4 hours no more nerves to improve the command ![]() .
.
THX,
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Norbert,
There is a smal issue in the one-liner. I had add "|grep -o false".
ifconfig -a |grep -B 1 inet |grep encap| awk '{print $1}' | grep -v lo | grep -v ":" | grep -v ^lo | xargs -I % sh -c 'echo %;echo -n " VIP "; cphaprob -a if |grep %|grep -v U|grep -v D | cut -c16-| tr -d "\r\n" ;echo;echo -n " IP ";ifconfig % | grep "inet addr" | cut -d ":" -f 2 | cut -d " " -f 1;echo -n " Mask " ;ifconfig % | sed -rn "2s/ .*:(.*)$/\1/p";echo -en " ANTISPOOFING ENABLED:\t";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep has_addr_info | cut -c17- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq ; echo -en " ANTISPOOFING MODE:\t"; if [ `more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep monitor_only | cut -c16- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq| grep -o false` ]; then echo "PREVENT"; else echo "DETECT"; fi; echo -en " ANTISPOOFING TOPO:\t"; if [ `more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set |grep -A 30 % | grep external | cut -c12- | tr \) " " |sort -ng| uniq| grep -o true` ]; then echo "External"; else echo "Internal"; fi;echo " ADDRESS SPOOFING NETWORKS:";more $FWDIR/state/local/FW1/local.set | grep -A 30 %|grep ": (\""|sort -ng| uniq |tr \(\)\<\>\:\" \ ;echo " "'
I also added the interface topology setting.

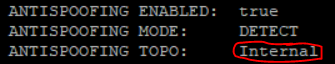
I think this is the longest one-liner in the forum ![]() .
.
For more infos see in this article with revisions:
Show Address Spoofing Networks via CLI
THX,
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
We can also add more fields.
:ifindex (3)
:span_port_interface (false)
:has_dir_scan_info (true)
:dir_scan_table (dir_scan_addrs_list4)
:has_addr_info (true)
:addr_table (valid_addrs_list4)
:mgmt_if_id (4)
:activate_mc_enforce (0)
:positive_mc_list (0)
:mc_log (0)
:overlap_nat (false)
:overlap_nat_src_addr ()
:overlap_nat_dst_addr ()
:overlap_nat_netmask (255.255.255.0)
:spooftrack (log)
:monitor_only (false)
:external (true)
:internal_type (undefined)
:access (undefined)
:dmz (false)
:mss_value (0)
I think "spooftrack" is intresting.
Or routing information of the interface
--> netstat -rn | grep <interface>
Do you want other fields?
Regards,
➜ CCSM Elite, CCME, CCTE ➜ www.checkpoint.tips
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Wow, where can I buy a copy of 'All Checkpoint Onliner Bash Commands' by: holder-of-the-keys, for $99.95?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Dear all,
I have tested you oneliner blindly during our saturday night, during an onsite migration 🙂
It's nearly perfect and but have only one limitation.
If there is multiple firewall on the policy target, they are all added to the local.set, and your oneliner only provide the first result;
meaning, firewall-Paris(single-GW) and firewall-Marseille(single-GW) are targets on the same package, the oneliner return the antispoofing policy of firewall-Paris on the firewall-Marseille
which let me think that firewall-marseille antispoofing was bad and makes me search for hours/days 🙂
I think (I'm terrible on scripting) that the problem on the oneliner is "sed '/ifindex 0/q'" which led to keep only the first part of the local.set.
regards,
Anthony
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Anthony,
thank you for this feedback. May I ask where you executed the One-liner? Management or Gateway?
Regards, Danny
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
local.set from the gateway(s).
on the SMS side, each GW has his how local.set, I checked md5sum.
the result is the same,
you can make a quick test, with a fake firewall, added to the same policy,
on the :if_info section, you'll get both firewall.
issue is: script will take the same first one 🙂
on the SMS side, each GW has his how local.set, I checked md5sum.
the result is the same,
you can make a quick test, with a fake firewall, added to the same policy,
on the :if_info section, you'll get both firewall.
issue is: script will take the same first one 🙂
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks, I improved the code.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I believe your test for VSX is incorrect:
if [[ $vsname != *'unavail'* ]]
It needs to be replaced in two places. The most reliable test I've found is this:
if [ $(ls /proc/vrf/ | wc -l) -gt 1 ]
/proc/vrf contains one subdirectory for every VRF on the system. There is always at least one VRF (0), so if the line count is greater than 1, there are multiple VRFs, so it's a VSX box.
SmartCenter R80.20 and up has already moved from VRFs to network namespaces, but as of R80.30, Firewall-1 has not. Still, it is likely to come in the future. This test should work for versions with use namespaces instead of VRFs:
if [ $(ip netns list | wc -l) -gt 1 ]
Edited to add: Also just noticed the two references to "$INSTANCE_VSID". That should probably be replaced with $(cat /proc/self/vrf). The $vsname and $INSTANCE_VSID variables are not set on older versions of VSX, while /proc/self/vrf is accurate on all versions which use VRFs.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Bob_Zimmerman ,
thank you for these suggestions. I have reviewed them and didn't update the One-liner yet because:
- $vsname is used 4 times, only replacing 2 occurences doesn't make sense and I didn't find an alternative method to get the name of a VS quickly without $vsname
- VRF's will change to namespaces soon while my One-liner is independent of both
- R77.30 support expires next month, so older versions of VSX are obsolete soon
Regards,
Danny
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The problem is $vsname doesn't even exist on non-VSX boxes. Thus, on non-VSX, it doesn't equal *'unavail'*, so the test always succeeds and takes the VSX path on non-VSX firewalls. The VSX path then tries to do things which don't work on non-VSX firewalls, such as looking for the value of $vsname (which, again, doesn't exist) in the local.set.
The script as it is does not work on non-VSX firewalls.
Edited to add: Also, it looks like $vsname isn't set when you initially log in to a VSX firewall. It's only set after the first vsenv.
Second edit: This combined test should work for both current VRF-based VSX and future netns-based VSX:
if [ $(ls /proc/vrf/ | wc -l) -gt 1 ] || [ $(ip netns list 2>/dev/null | wc -l) -gt 1 ]The STDERR redirection is needed because on pre-3.10 firewalls, 'ip netns' fails and prints an error.
Leaderboard
Epsum factorial non deposit quid pro quo hic escorol.
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 9 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |
Upcoming Events
Tue 22 Jul 2025 @ 10:00 AM (CEST)
Cyber Security Training in the Era of AI Threats: Managed SmartAwareness Explained - EMEATue 22 Jul 2025 @ 05:00 PM (CEST)
Cyber Security Training in the Era of AI Threats: Managed SmartAwareness Explained - AMERThu 24 Jul 2025 @ 11:00 AM (EDT)
Tips and Tricks 2025 #10: SD-WAN + Security: The Ultimate Defense for Your BusinessThu 31 Jul 2025 @ 10:00 AM (CEST)
CloudGuard Network Security for Nutanix - Full Deployment with Tenant & Transit VPC - EMEA/APACThu 31 Jul 2025 @ 05:00 PM (CEST)
CloudGuard Network Security for Nutanix - Full Deployment with Tenant & Transit VPC - AMER/EMEAWed 13 Aug 2025 @ 04:00 PM (CEST)
Operationalizing Threat Intelligence, Part III: Threat Modeling & Security PreparednessTue 22 Jul 2025 @ 10:00 AM (CEST)
Cyber Security Training in the Era of AI Threats: Managed SmartAwareness Explained - EMEATue 22 Jul 2025 @ 05:00 PM (CEST)
Cyber Security Training in the Era of AI Threats: Managed SmartAwareness Explained - AMERThu 24 Jul 2025 @ 11:00 AM (EDT)
Tips and Tricks 2025 #10: SD-WAN + Security: The Ultimate Defense for Your BusinessThu 31 Jul 2025 @ 10:00 AM (CEST)
CloudGuard Network Security for Nutanix - Full Deployment with Tenant & Transit VPC - EMEA/APACThu 31 Jul 2025 @ 05:00 PM (CEST)
CloudGuard Network Security for Nutanix - Full Deployment with Tenant & Transit VPC - AMER/EMEAWed 13 Aug 2025 @ 04:00 PM (CEST)
Operationalizing Threat Intelligence, Part III: Threat Modeling & Security PreparednessAbout CheckMates
Learn Check Point
Advanced Learning
YOU DESERVE THE BEST SECURITY
©1994-2025 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved.
Copyright
Privacy Policy
About Us
UserCenter


